Contribution of bioinformatics prediction in microRNA-based cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 25450261
- PMCID: PMC4277182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.030
Contribution of bioinformatics prediction in microRNA-based cancer therapeutics
Abstract
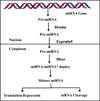
Despite enormous efforts, cancer remains one of the most lethal diseases in the world. With the advancement of high throughput technologies massive amounts of cancer data can be accessed and analyzed. Bioinformatics provides a platform to assist biologists in developing minimally invasive biomarkers to detect cancer, and in designing effective personalized therapies to treat cancer patients. Still, the early diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of cancer are an open challenge for the research community. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that serve to regulate gene expression. The discovery of deregulated miRNAs in cancer cells and tissues has led many to investigate the use of miRNAs as potential biomarkers for early detection, and as a therapeutic agent to treat cancer. Here we describe advancements in computational approaches to predict miRNAs and their targets, and discuss the role of bioinformatics in studying miRNAs in the context of human cancer.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Computational model; MiRNAs; MicroRNAs; Pancreatic cancer; Therapy.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

