2',3'-cAMP, 3'-AMP, 2'-AMP and adenosine inhibit TNF-α and CXCL10 production from activated primary murine microglia via A2A receptors
- PMID: 25451117
- PMCID: PMC4262711
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.059
2',3'-cAMP, 3'-AMP, 2'-AMP and adenosine inhibit TNF-α and CXCL10 production from activated primary murine microglia via A2A receptors
Abstract
Background: Some cells, tissues and organs release 2',3'-cAMP (a positional isomer of 3',5'-cAMP) and convert extracellular 2',3'-cAMP to 2'-AMP plus 3'-AMP and convert these AMPs to adenosine (called the extracellular 2',3'-cAMP-adenosine pathway). Recent studies show that microglia have an extracellular 2',3'-cAMP-adenosine pathway. The goal of the present study was to investigate whether the extracellular 2',3'-cAMP-adenosine pathway could have functional consequences on the production of cytokines/chemokines by activated microglia.
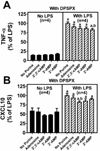
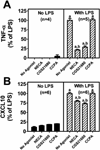
Methods: Experiments were conducted in cultures of primary murine microglia. In the first experiment, the effect of 2',3'-cAMP, 3'-AMP, 2'-AMP and adenosine on LPS-induced TNF-α and CXCL10 production was determined. In the next experiment, the first protocol was replicated but with the addition of 1,3-dipropyl-8-p-sulfophenylxanthine (DPSPX) (0.1 μM; antagonist of adenosine receptors). The last experiment compared the ability of 2-chloro-N(6)-cyclopentyladenosine (CCPA) (10 μM; selective A1 agonist), 5'-N-ethylcarboxamide adenosine (NECA) (10 μM; agonist for all adenosine receptor subtypes) and CGS21680 (10 μM; selective A2A agonist) to inhibit LPS-induced TNF-α and CXCL10 production.
Results: (1) 2',3'-cAMP, 3'-AMP, 2'-AMP and adenosine similarly inhibited LPS-induced TNF-α and CXCL10 production; (2) DPSPX nearly eliminated the inhibitory effects of 2',3'-cAMP, 3'-AMP, 2'-AMP and adenosine on LPS-induced TNF-α and CXCL10 production; (3) CCPA did not affect LPS-induced TNF-α and CXCL10; (4) NECA and CGS21680 similarly inhibited LPS-induced TNF-α and CXCL10 production.
Conclusions: 2',3'-cAMP and its metabolites (3'-AMP, 2'-AMP and adenosine) inhibit LPS-induced TNF-α and CXCL10 production via A2A-receptor activation. Adenosine and its precursors, via A2A receptors, likely suppress TNF-α and CXCL10 production by activated microglia in brain diseases.
Keywords: 2′,3′-cAMP; 2′-AMP; 3′-AMP; A(2A) receptors; Adenosine; Adenosine receptors; CXCL10; Primary microglia; TNF.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F. Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science. 2005;308(5726):1314–1318. - PubMed
-
- Kreutzberg GW. Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19(8):312–318. - PubMed
-
- Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(1):57–69. - PubMed
-
- Butovsky O, et al. Microglia activated by IL-4 or IFN-gamma differentially induce neurogenesis and oligodendrogenesis from adult stem/progenitor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006;31(1):149–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK068575/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL069846/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069846/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087978/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091190/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD040686/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK091190/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL109002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK068575/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD040686/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS087978/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

