A long-term intensive lifestyle intervention and physical function: the look AHEAD Movement and Memory Study
- PMID: 25452229
- PMCID: PMC4276480
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.20944
A long-term intensive lifestyle intervention and physical function: the look AHEAD Movement and Memory Study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the long-term effects of an intensive lifestyle intervention on physical function using a randomized post-test design in the Look AHEAD trial.
Methods: Overweight and obese (BMI ≥ 25 kg m(-2)) middle-aged and older adults (aged 45-76 years at enrollment) with type 2 diabetes (n = 964) at four clinics in Look AHEAD, a trial evaluating an intensive lifestyle intervention (ILI) designed to achieve weight loss through caloric restriction and increased physical activity compared to diabetes support and education (DSE), underwent standardized assessments of performance-based physical function including an expanded short physical performance battery (SPPBexp ), 20-m and 400-m walk, and grip and knee extensor strength 8 years post-randomization, during the trial's weight maintenance phase.
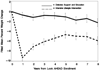
Results: Eight years post-randomization, individuals randomized to ILI had better SPPBexp scores [adjusted mean (SE) difference: 0.055 (0.022), P = 0.01] and faster 20-m and 400-m walk speeds [0.032 (0.012) m s(-1) , P = 0.01, and 0.025 (0.011) m s(-1) , P = 0.02, respectively] compared to those randomized to DSE. Achieved weight loss greatly attenuated the group differences in physical function, and the intervention effect was no longer significant.
Conclusions: An intensive lifestyle intervention has long-term benefits for mobility function in overweight and obese middle-aged and older individuals with type 2 diabetes.
© 2014 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Guralnik JM, Fried LP, Salive ME. Disability as a public health outcome in the aging population. Annu Rev Public Health. 1996;17:25–46. - PubMed
-
- Fried LP, Guralnik JM. Disability in older adults: evidence regarding significance, etiology, and risk. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997;45(1):92–100. - PubMed
-
- Vincent HK, Vincent KR, Lamb KM. Obesity and mobility disability in the older adult. Obes Rev. 2010;11(8):568–579. - PubMed
-
- Jensen GL, Hsiao PY. Obesity in older adults: relationship to functional limitation. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2010;13(1):46–51. - PubMed
-
- Figaro MK, Kritchevsky SB, Resnick HE, et al. Diabetes, inflammation, and functional decline in older adults: findings from the Health, Aging and Body Composition (ABC) study. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(9):2039–2045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- DK57078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG024827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG03308701/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK57151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033087/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK57149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG21332/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK48520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DK57177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001120/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR0021140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK 046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021332/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR 024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK56992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical