Low-level laser therapy attenuates LPS-induced rats mastitis by inhibiting polymorphonuclear neutrophil adhesion
- PMID: 25452258
- PMCID: PMC4272976
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.14-0061
Low-level laser therapy attenuates LPS-induced rats mastitis by inhibiting polymorphonuclear neutrophil adhesion
Abstract
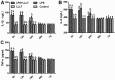
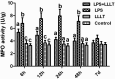
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on a rat model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mastitis and its underlying molecular mechanisms. The rat model of mastitis was induced by inoculation of LPS through the canals of the mammary gland. The results showed that LPS-induced secretion of IL-1β and IL-8 significantly decreased after LLLT (650 nm, 2.5 mW, 30 mW/cm(2)). LLLT also inhibited intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression and attenuated the LPS-induced decrease of the expression of CD62L and increase of the expression of CD11b. Moreover, LLLT also suppressed LPS-induced polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) entering the alveoli of the mammary gland. The number of PMNs in the mammary alveolus and the myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity were decreased after LLLT. These results suggested that LLLT therapy is beneficial in decreasing the somatic cell count and improving milk nutritional quality in cows with an intramammary infection.
Figures
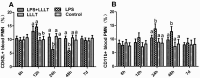



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the changes of immune cells during lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis in rats.Cytokine. 2007 Nov;40(2):135-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.08.012. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Cytokine. 2007. PMID: 17967544
-
Low intensity laser therapy (LILT) in vivo acts on the neutrophils recruitment and chemokines/cytokines levels in a model of acute pulmonary inflammation induced by aerosol of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli in rat.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2010 Dec 2;101(3):271-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.07.012. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2010. PMID: 20728373
-
Effect of low-level laser therapy on the expression of inflammatory mediators and on neutrophils and macrophages in acute joint inflammation.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5):R116. doi: 10.1186/ar4296. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24028507 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intramammary administration of prednisolone on the blood-milk barrier during the immune response of the mammary gland to lipopolysaccharide.Am J Vet Res. 2014 Jun;75(6):595-601. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.75.6.595. Am J Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 24866517
-
Low level laser therapy (LLLT) decreases pulmonary microvascular leakage, neutrophil influx and IL-1beta levels in airway and lung from rat subjected to LPS-induced inflammation.Inflammation. 2008 Jun;31(3):189-97. doi: 10.1007/s10753-008-9064-4. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Inflammation. 2008. PMID: 18421573
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Berberine Hydrochloride in an LPS-Induced Murine Model of Mastitis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Apr 15;2018:5164314. doi: 10.1155/2018/5164314. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29849710 Free PMC article.
-
Pedunculoside protects against LPS-induced mastitis in mice by inhibiting inflammation and maintaining the integrity of blood-milk barrier.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Aug 12;13(15):19460-19474. doi: 10.18632/aging.203357. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34383710 Free PMC article.
-
Low-level laser therapy stimulates the oxidative burst in human neutrophils and increases their fungicidal capacity.J Biophotonics. 2016 Dec;9(11-12):1180-1188. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201600035. Epub 2016 May 31. J Biophotonics. 2016. PMID: 27243910 Free PMC article.
-
The Probable Protective Effect of Photobiomodulation on the Immunologic Factor's mRNA Expression Level in the Lung: An Extended COVID-19 Preclinical and Clinical Meta-analysis.Clin Pathol. 2023 Mar 13;16:2632010X221127683. doi: 10.1177/2632010X221127683. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Clin Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36938515 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aimbire F., Ligeiro de Oliveira A. P., Albertini R., Corrêa J. C., Ladeira de Campos C. B., Lyon J. P., Silva J. A., Jr, Costa M. S.2008. Low level laser therapy (LLLT) decreases pulmonary microvascular leakage, neutrophil influx and IL-1beta levels in airway and lung from rat subjected to LPS-induced inflammation. Inflammation 31: 189–197. doi: 10.1007/s10753-008-9064-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alves A. C., Vieira R. D., Leal-Junior E. C., Dos Santos S. A., Ligeiro A. P., Albertini R., Junior J. A., de Carvalho P. D.2013. Effect of low-level laser therapy on the expression of inflammatory mediators and on neutrophils and macrophages in acute joint inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 15: R116. doi: 10.1186/ar4296 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beneduci A., Chidichimo G., Nappi M. C., Rossi R., Turco R., Lucifora G., Garrafa F.2007. Evaluation of the effects induced by near infrared low intensity laser radiation on bovines affected by subacute mastitis: a single-quarter foremilk sampling study. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 6: 761–767.
-
- Bjordal J. M., Lopes-Martins R. A. B., Joensen J., Iversen V. V.2010. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of low level laser therapy and its relevance for clinical use in physiotherapy. Phys. Ther. Rev. 15: 286–293. doi: 10.1179/1743288X10Y.0000000001 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

