A retrospective analysis of the clinicopathological characteristics of large cell carcinoma of the lung
- PMID: 25452802
- PMCID: PMC4247287
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.2075
A retrospective analysis of the clinicopathological characteristics of large cell carcinoma of the lung
Abstract
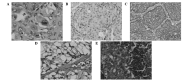
The aim of the present study was to analyze and summarize the clinicopathological characteristics of large-cell lung carcinoma (LCLC) of the lung, in order to improve the definite diagnosis rate of LCLC. Clinicopathological data of 174 patients with LCLC, confirmed pathologically, were retrospectively reviewed. The 174 cases of LCLC accounted for 5.7% of the total lung cancer cases during the corresponding time period at the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Tianjin Medical University (Tianjin, China), among which there were 131 males and 43 females with an average age of 61.4 years. The postoperative pathological diagnosis of the 174 cases showed 80 cases of classic LCLC, 64 cases of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC), six cases of combined LCNEC, 19 cases of basaloid carcinoma, three cases of clear cell carcinoma and two cases of lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma. Of the total 174 LCLC cases, 96 patients exhibited lymph node metastasis. LCLC is a highly aggressive malignancy with a high tendency of invasion and metastasis, although the incidence rate is low. A definite diagnosis of LCLC primarily relies on the pathological diagnosis. Each subtype of LCLC has its own pathomorphological and immunohistochemical characteristics.
Keywords: large cell carcinoma; lung cancer; pathology; retrospective analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gene Expression Profiling of Large Cell Lung Cancer Links Transcriptional Phenotypes to the New Histological WHO 2015 Classification.J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Aug;12(8):1257-1267. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.05.008. Epub 2017 May 20. J Thorac Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28535939
-
Whole-genome characterization of large-cell lung carcinoma: A comparative analysis based on the histological classification.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 4;13:1070048. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1070048. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36685819 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of the clinical characteristics and the pathology of large cell lung cancer].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 1999 Jul;22(7):401-3. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 1999. PMID: 11775810 Chinese.
-
Treatment of lung large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7047-57. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5003-4. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26943800 Review.
-
Clinical analysis of small cell carcinoma of the bladder in Chinese: nine case reports and literature reviews.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 Jan 26;15(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-1079-y. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28125986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinicopathological characteristics, treatment and survival of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a SEER population-based study.PeerJ. 2019 Mar 27;7:e6539. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6539. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30944773 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Chemotherapy in Stage II-IV Large-Cell Lung Carcinoma and Construction of Its Predictive Nomograms: A SEER Analysis.Med Princ Pract. 2023;32(1):49-60. doi: 10.1159/000529202. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Med Princ Pract. 2023. PMID: 36652925 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological features and prognosis of primary pulmonary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Sep;8(9):2610-2616. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.08.40. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 27747015 Free PMC article.
-
Primary pulmonary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma in non-endemic region: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Feb;97(8):e9976. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009976. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29465599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of a novel nomogram to predict the overall survival of patients with large cell lung cancer: A surveillance, epidemiology, and end results population-based study.Heliyon. 2023 May 6;9(5):e15924. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15924. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37223713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK, Harris CC, editors. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. IARC Press; Lyon: 2004. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours.
-
- Zhang J, Yu JP, Yu WW, et al. Relationship between VEGF expression and dendritic cells and regulatory T cell distribution in large cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Liu Lin Chuang. 2012;39:1501–1504. (In Chinese)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
