Effect of baseline HbA1c level on the development of diabetes by lifestyle intervention in primary healthcare settings: insights from subanalysis of the Japan Diabetes Prevention Program
- PMID: 25452854
- PMCID: PMC4212559
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2013-000003
Effect of baseline HbA1c level on the development of diabetes by lifestyle intervention in primary healthcare settings: insights from subanalysis of the Japan Diabetes Prevention Program
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the effects of a lifestyle intervention on the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) among participants with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), in particular in the subgroup with baseline glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels ≥5.7%, in primary healthcare settings.
Design: Randomized controlled trial.
Setting: 32 healthcare centers in Japan.
Participants: Participants with IGT, aged 30-60 years, were randomly assigned to either an intensive lifestyle intervention group (ILG) or a usual care group (UCG).
Interventions: During the initial 6 months, participants in the ILG received four group sessions on healthy lifestyles by public health providers. An individual session was further conducted biannually during the 3 years. Participants in the UCG received usual care such as one group session on healthy lifestyles.
Outcome measures: The primary endpoint was the development of T2DM based on an oral glucose tolerance test.
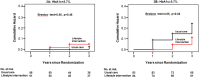
Results: The mean follow-up period was 2.3 years. The annual incidence of T2DM were 2.7 and 5.1/100 person-years of follow-up in the ILG (n=145) and UCG (n=149), respectively. The cumulative incidence of T2DM was significantly lower in the ILG than in the UCG among participants with HbA1c levels ≥5.7% (log-rank=3.52, p=0.06; Breslow=4.05, p=0.04; Tarone-Ware=3.79, p=0.05), while this was not found among participants with HbA1c levels <5.7%.
Conclusions: Intensive lifestyle intervention in primary healthcare setting is effective in preventing the development of T2DM in IGT participants with HbA1c levels ≥5.7%, relative to those with HbA1c levels <5.7%.
Trial registration number: UMIN000003136.
Keywords: HbA1c; Impaired Glucose Tolerance; Intervention Groups; Type 2 Diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Ginter E, Simko V. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, pandemic in 21st century. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012;771:42–50 - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, et al. . Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 2001;344: 1343–92 - PubMed
-
- Kuroe A, Fukushima M, Usami M, et al. . Impaired beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in Japanese subjects with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2003;59: 71–7 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources