Nanoclustering as a dominant feature of plasma membrane organization
- PMID: 25453114
- PMCID: PMC4260763
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.146340
Nanoclustering as a dominant feature of plasma membrane organization
Abstract
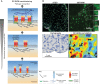
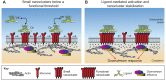
Early studies have revealed that some mammalian plasma membrane proteins exist in small nanoclusters. The advent of super-resolution microscopy has corroborated and extended this picture, and led to the suggestion that many, if not most, membrane proteins are clustered at the plasma membrane at nanoscale lengths. In this Commentary, we present selected examples of glycosylphosphatidyl-anchored proteins, Ras family members and several immune receptors that provide evidence for nanoclustering. We advocate the view that nanoclustering is an important part of the hierarchical organization of proteins in the plasma membrane. According to this emerging picture, nanoclusters can be organized on the mesoscale to form microdomains that are capable of supporting cell adhesion, pathogen binding and immune cell-cell recognition amongst other functions. Yet, a number of outstanding issues concerning nanoclusters remain open, including the details of their molecular composition, biogenesis, size, stability, function and regulation. Notions about these details are put forth and suggestions are made about nanocluster function and why this general feature of protein nanoclustering appears to be so prevalent.
Keywords: Plasma membrane; Protein nanoclustering; Super-resolution microscopy.
© 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Bakker G. J., Eich C., Torreno-Pina J. A., Diez-Ahedo R., Perez-Samper G., van Zanten T. S., Figdor C. G., Cambi A., Garcia-Parajo M. F. (2012). Lateral mobility of individual integrin nanoclusters orchestrates the onset for leukocyte adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 4869–4874 10.1073/pnas.1116425109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cambi A., de Lange F., van Maarseveen N. M., Nijhuis M., Joosten B., van Dijk E. M. H. P., de Bakker B. I., Fransen J. A. M., Bovee-Geurts P. H. M., van Leeuwen F. N. et al. (2004). Microdomains of the C-type lectin DC-SIGN are portals for virus entry into dendritic cells. J. Cell Biol. 164, 145–155 10.1083/jcb.200306112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

