Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease: genetic, immunological, and clinical features of inborn errors of IFN-γ immunity
- PMID: 25453225
- PMCID: PMC4357480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.09.008
Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease: genetic, immunological, and clinical features of inborn errors of IFN-γ immunity
Abstract
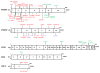
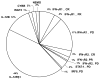
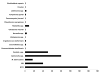
Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD) is a rare condition characterized by predisposition to clinical disease caused by weakly virulent mycobacteria, such as BCG vaccines and environmental mycobacteria, in otherwise healthy individuals with no overt abnormalities in routine hematological and immunological tests. MSMD designation does not recapitulate all the clinical features, as patients are also prone to salmonellosis, candidiasis and tuberculosis, and more rarely to infections with other intramacrophagic bacteria, fungi, or parasites, and even, perhaps, a few viruses. Since 1996, nine MSMD-causing genes, including seven autosomal (IFNGR1, IFNGR2, STAT1, IL12B, IL12RB1, ISG15, and IRF8) and two X-linked (NEMO, and CYBB) genes have been discovered. The high level of allelic heterogeneity has already led to the definition of 18 different disorders. The nine gene products are physiologically related, as all are involved in IFN-γ-dependent immunity. These disorders impair the production of (IL12B, IL12RB1, IRF8, ISG15, NEMO) or the response to (IFNGR1, IFNGR2, STAT1, IRF8, CYBB) IFN-γ. These defects account for only about half the known MSMD cases. Patients with MSMD-causing genetic defects may display other infectious diseases, or even remain asymptomatic. Most of these inborn errors do not show complete clinical penetrance for the case-definition phenotype of MSMD. We review here the genetic, immunological, and clinical features of patients with inborn errors of IFN-γ-dependent immunity.
Keywords: BCG; IFN-γ; IL-12; ISG15; Mycobacteriosis; Primary immunodeficiency; Tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or commercial conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Casanova JL, Abel L. Genetic dissection of immunity to mycobacteria: the human model. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:581–620. - PubMed
-
- Levin M, Newport MJ, D’Souza S, Kalabalikis P, Brown IN, Lenicker HM, Agius PV, Davies EG, Thrasher A, Klein N, et al. Familial disseminated atypical mycobacterial infection in childhood: a human mycobacterial susceptibility gene? Lancet. 1995;345(8942):79–83. - PubMed
-
- Casanova JL, Jouanguy E, Lamhamedi S, Blanche S, Fischer A. Immunological conditions of children with BCG disseminated infection. Lancet. 1995;346(8974):581. - PubMed
-
- Mimouni J. Our experiences in three years of BCG vaccination at the center of the O.P.H.S. at Constantine; study of observed cases (25 cases of complications from BCG vaccination) Alger Medicale. 1951;55(8):1138–1147. - PubMed
-
- Ulgenalp I, Yalcin M, Cetiner M, Ozgen M, Koseli I. Olumle sonuclanan jeneralize BCG enfeksiyonu. Tuberculoz ve Toraks. 1973;21:11–19.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

