Linear regression analysis of Hospital Episode Statistics predicts a large increase in demand for elective hand surgery in England
- PMID: 25455287
- PMCID: PMC4315884
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjps.2014.10.011
Linear regression analysis of Hospital Episode Statistics predicts a large increase in demand for elective hand surgery in England
Abstract
Introduction: We integrated two factors, demographic population shifts and changes in prevalence of disease, to predict future trends in demand for hand surgery in England, to facilitate workforce planning.
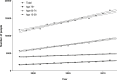
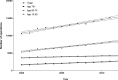
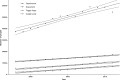
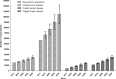
Methods: We analysed Hospital Episode Statistics data for Dupuytren's disease, carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome, and trigger finger from 1998 to 2011. Using linear regression, we estimated trends in both diagnosis and surgery until 2030. We integrated this regression with age specific population data from the Office for National Statistics in order to estimate how this will contribute to a change in workload over time.
Results: There has been a significant increase in both absolute numbers of diagnoses and surgery for all four conditions. Combined with future population data, we calculate that the total operative burden for these four conditions will increase from 87,582 in 2011 to 170,166 (95% confidence interval 144,517-195,353) in 2030.
Discussion: The prevalence of these diseases in the ageing population, and increasing prevalence of predisposing factors such as obesity and diabetes, may account for the predicted increase in workload. The most cost effective treatments must be sought, which requires high quality clinical trials. Our methodology can be applied to other sub-specialties to help anticipate the need for future service provision.
Keywords: Carpal tunnel; Cubital tunnel; Dupuytren's disease; Incidence; Trigger finger; Workforce planning.
Copyright © 2014 British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- BSSH working party . 2007. Hand surgery in the UK: manpower, resources, standards and training.http://www.bssh.ac.uk/members/documents/ukhandsurgreport.pdf [accessed 08.02.14]
-
- UK parliamentary health care enquiry . Short Memorandum of Evidence Prepared by the Royal College of Surgeons of England; 2006. Workforce needs and planning for the health service.http://www.rcseng.ac.uk/publications/docs/rcseng_enquiry_workforce.html [accessed 08.02.14]
-
- The Royal College of Surgeons of England. Surgical workforce 2010: profile and trends. http://www.rcseng.ac.uk/publications/docs/surgical-workforce-2010-profil... [accessed 08.02.14].
-
- Tseng C.H., Liao C.C., Kuo C.M., Sung F.C., Hsieh D.P., Tsai C.H. Medical and non-medical correlates of carpal tunnel syndrome in a Taiwan cohort of one million. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19:91–97. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

