A meta-analytic review of the effects of exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PMID: 25455510
- PMCID: PMC4314337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.10.003
A meta-analytic review of the effects of exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Abstract
Consistent evidence indicates that exercise improves cognition and mood, with preliminary evidence suggesting that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) may mediate these effects. The aim of the current meta-analysis was to provide an estimate of the strength of the association between exercise and increased BDNF levels in humans across multiple exercise paradigms. We conducted a meta-analysis of 29 studies (N = 1111 participants) examining the effect of exercise on BDNF levels in three exercise paradigms: (1) a single session of exercise, (2) a session of exercise following a program of regular exercise, and (3) resting BDNF levels following a program of regular exercise. Moderators of this effect were also examined. Results demonstrated a moderate effect size for increases in BDNF following a single session of exercise (Hedges' g = 0.46, p < 0.001). Further, regular exercise intensified the effect of a session of exercise on BDNF levels (Hedges' g = 0.59, p = 0.02). Finally, results indicated a small effect of regular exercise on resting BDNF levels (Hedges' g = 0.27, p = 0.005). When analyzing results across paradigms, sex significantly moderated the effect of exercise on BDNF levels, such that studies with more women showed less BDNF change resulting from exercise. Effect size analysis supports the role of exercise as a strategy for enhancing BDNF activity in humans, but indicates that the magnitude of these effects may be lower in females relative to males.
Keywords: BDNF; Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Exercise; Meta-analysis; Physical activity.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
In the past 3 years Dr. Otto has served as a paid consultant for MicroTransponder Inc., Concert Pharmaceuticals, and ProPhase; provided expert consensus opinion for Otsuka Pharmaceuticals; received royalty support for use of the SIGH-A from ProPhase; and received book royalties from Oxford University Press, Routledge, and Springer. The other authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures

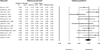
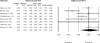
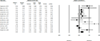
References
-
- Alford L. What men should know about the impact of physical activity on their health. International journal of clinical practice. 2010;64:1731–1734. - PubMed
-
- Altar CA. Neurotrophins and depression. Trends in pharmacological sciences. 1999;20:59–62. - PubMed
-
- Angelucci F, Gelfo F, De Bartolo P, Caltagirone C, Petrosini L. BDNF concentrations are decreased in serum and parietal cortex in immunotoxin 192 IgG-Saporin rat model of cholinergic degeneration. Neurochemistry international. 2011;59:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Araya AV, Orellana X, Godoy D, Soto L, Fiedler J. Effect of exercise on circulating levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in overweight and obese subjects. Hormone and metabolic research. 2013;45:541–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

