The two faces of receptor interacting protein kinase-1
- PMID: 25459879
- PMCID: PMC4254517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.11.001
The two faces of receptor interacting protein kinase-1
Abstract
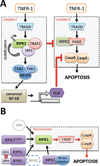
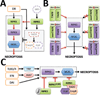
Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase-1 (RIPK1), a key player in inflammation and cell death, assumes opposite functions depending on the cellular context and its posttranslational modifications. Genetic evidence supported by biochemical and cellular biology approaches sheds light on the circumstances in which RIPK1 promotes or inhibits these processes.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

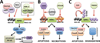
References
-
- Balachandran S, Thomas E, Barber GN. A FADD-dependent innate immune mechanism in mammalian cells. Nature. 2004;432:401–405. - PubMed
-
- Belz K, Schoeneberger H, Wehner S, Weigert A, Bönig H, Klingebiel T, Fichtner I, Fulda S. Smac mimetic and glucocorticoids synergize to induce apoptosis in childhood ALL by promoting ripoptosome assembly. Blood. 2014;124:240–250. - PubMed
-
- Berger SB, Kasparcova V, Hoffman S, Swift B, Dare L, Schaeffer M, Capriotti C, Cook M, Finger J, Hughes-Earle A, et al. Cutting Edge: RIP1 kinase activity is dispensable for normal development but is a key regulator of inflammation in SHARPIN-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 2014;192:5476–5480. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertrand MJM, Milutinovic S, Dickson KM, Ho WC, Boudreault A, Durkin J, Gillard JW, Jaquith JB, Morris SJ, Barker PA. cIAP1 and cIAP2 Facilitate Cancer Cell Survival by Functioning as E3 Ligases that Promote RIP1 Ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. 2008;30:689–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

