Ketogenic diets as an adjuvant cancer therapy: History and potential mechanism
- PMID: 25460731
- PMCID: PMC4215472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.08.002
Ketogenic diets as an adjuvant cancer therapy: History and potential mechanism
Abstract
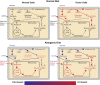
Cancer cells, relative to normal cells, demonstrate significant alterations in metabolism that are proposed to result in increased steady-state levels of mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as O2(•-)and H2O2. It has also been proposed that cancer cells increase glucose and hydroperoxide metabolism to compensate for increased levels of ROS. Given this theoretical construct, it is reasonable to propose that forcing cancer cells to use mitochondrial oxidative metabolism by feeding ketogenic diets that are high in fats and low in glucose and other carbohydrates, would selectively cause metabolic oxidative stress in cancer versus normal cells. Increased metabolic oxidative stress in cancer cells would in turn be predicted to selectively sensitize cancer cells to conventional radiation and chemotherapies. This review summarizes the evidence supporting the hypothesis that ketogenic diets may be safely used as an adjuvant therapy to conventional radiation and chemotherapies and discusses the proposed mechanisms by which ketogenic diets may enhance cancer cell therapeutic responses.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Ketogenic diet; Oxidative stress.
© 2014 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad I.M., Aykin-Burns N., Sim J.E., Walsh S.A., Higashikubo R., Buettner G.R., Venkataraman S., Mackey M.A., Flanagan S.W., Oberley L.W., Spitz D.R. Mitochondrial O2•− and H2O2 mediate glucose deprivation-induced stress in human cancer cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280(6):4254–4263. 15561720 - PubMed
-
- Allen B.G., Bhatia S.K., Buatti J.M., Brandt K.E., Lindholm K.E., Button A.M., Szweda L.I., Smith B.J., Spitz D.R., Fath M.A. Ketogenic diets enhance oxidative stress and radio-chemo-therapy responses in lung cancer xenografts. Clinical Cancer Research: 2013;19(14):3905–3913. 23743570 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

