Computer-generated vs. physician-documented history of present illness (HPI): results of a blinded comparison
- PMID: 25461620
- PMCID: PMC4289091
- DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2014.356
Computer-generated vs. physician-documented history of present illness (HPI): results of a blinded comparison
Abstract
Objectives: Healthcare delivery now mandates shorter visits with higher documentation requirements, undermining the patient-provider interaction. To improve clinic visit efficiency, we developed a patient-provider portal that systematically collects patient symptoms using a computer algorithm called Automated Evaluation of Gastrointestinal Symptoms (AEGIS). AEGIS also automatically "translates" the patient report into a full narrative history of present illness (HPI). We aimed to compare the quality of computer-generated vs. physician-documented HPIs.
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional study with a paired sample design among individuals visiting outpatient adult gastrointestinal (GI) clinics for evaluation of active GI symptoms. Participants first underwent usual care and then subsequently completed AEGIS. Each individual thereby had both a physician-documented and a computer-generated HPI. Forty-eight blinded physicians assessed HPI quality across six domains using 5-point scales: (i) overall impression, (ii) thoroughness, (iii) usefulness, (iv) organization, (v) succinctness, and (vi) comprehensibility. We compared HPI scores within patient using a repeated measures model.
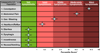
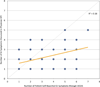
Results: Seventy-five patients had both computer-generated and physician-documented HPIs. The mean overall impression score for computer-generated HPIs was higher than physician HPIs (3.68 vs. 2.80; P<0.001), even after adjusting for physician and visit type, location, mode of transcription, and demographics. Computer-generated HPIs were also judged more complete (3.70 vs. 2.73; P<0.001), more useful (3.82 vs. 3.04; P<0.001), better organized (3.66 vs. 2.80; P<0.001), more succinct (3.55 vs. 3.17; P<0.001), and more comprehensible (3.66 vs. 2.97; P<0.001).
Conclusions: Computer-generated HPIs were of higher overall quality, better organized, and more succinct, comprehensible, complete, and useful compared with HPIs written by physicians during usual care in GI clinics.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

References
-
- Blumenthal D. Launching HITECH. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:382–385. - PubMed
-
- Handler T, Holtmeier R, Metzger J, et al. HIMSS electronic health record definitional model version 1.0. The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) Electronic Health Record Committee; 2003.
-
- DesRoches CM, Charles D, Furukawa MF, et al. Adoption of electronic health records grows rapidly, but fewer than half of US hospitals had at least a basic system in 2012. Health Aff (Millwood) 2013;32:1478–1485. - PubMed
-
- Goldzweig CL, Towfigh A, Maglione M, et al. Costs and benefits of health information technology: new trends from the literature. Health Aff (Millwood) 2009;28:w282–w293. - PubMed
-
- van der Lei J, Moorman PW, Musen MA. Electronic patient records in medical practice: a multidisciplinary endeavor. Methods Inf Med. 1999;38:287–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

