An MHC class I immune evasion gene of Marek׳s disease virus
- PMID: 25462349
- PMCID: PMC4280340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.11.008
An MHC class I immune evasion gene of Marek׳s disease virus
Abstract
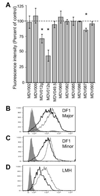
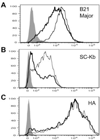
Marek׳s disease virus (MDV) is a widespread α-herpesvirus of chickens that causes T cell tumors. Acute, but not latent, MDV infection has previously been shown to lead to downregulation of cell-surface MHC class I (Virology 282:198-205 (2001)), but the gene(s) involved have not been identified. Here we demonstrate that an MDV gene, MDV012, is capable of reducing surface expression of MHC class I on chicken cells. Co-expression of an MHC class I-binding peptide targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum (bypassing the requirement for the TAP peptide transporter) partially rescued MHC class I expression in the presence of MDV012, suggesting that MDV012 is a TAP-blocking MHC class I immune evasion protein. This is the first unique non-mammalian MHC class I immune evasion gene identified, and suggests that α-herpesviruses have conserved this function for at least 100 million years.
Keywords: Immune evasion; Major histocompatibility complex class I; Marek׳s disease virus.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Atkins KE, Read AF, Savill NJ, Renz KG, Islam AF, Walkden-Brown SW, Woolhouse MEJ. Vaccination and reduced cohort duration can drive virulence evolution: Marek’s disease virus and industrialized agriculture. Evolution. 2013;67:851–860. - PubMed
-
- Bachmair A, Finley D, Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986;234:179–186. - PubMed
-
- Briles WE, Stone HA, Cole RK. Marek's disease: effects of B histocompatibility alloalleles in resistant and susceptible chicken lines. Science. 1977;195:193–195. - PubMed
-
- Burgos JS, Serrano-Saiz E, Sastre I, Valdivieso F. ICP47 mediates viral neuroinvasiveness by induction of TAP protein following intravenous inoculation of herpes simplex virus type 1 in mice. J. Neurovirol. 2006;12:420–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

