Identification of the remains of King Richard III
- PMID: 25463651
- PMCID: PMC4268703
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6631
Identification of the remains of King Richard III
Abstract
In 2012, a skeleton was excavated at the presumed site of the Grey Friars friary in Leicester, the last-known resting place of King Richard III. Archaeological, osteological and radiocarbon dating data were consistent with these being his remains. Here we report DNA analyses of both the skeletal remains and living relatives of Richard III. We find a perfect mitochondrial DNA match between the sequence obtained from the remains and one living relative, and a single-base substitution when compared with a second relative. Y-chromosome haplotypes from male-line relatives and the remains do not match, which could be attributed to a false-paternity event occurring in any of the intervening generations. DNA-predicted hair and eye colour are consistent with Richard's appearance in an early portrait. We calculate likelihood ratios for the non-genetic and genetic data separately, and combined, and conclude that the evidence for the remains being those of Richard III is overwhelming.
Figures
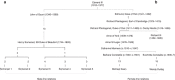

References
-
- Rous J. Joannis Rossi antiquiarii Wawicensis Historia Regum Angliae Oxford: Theatro Sheldoniano (1745) [1486]).
-
- Speed J. The History of Great Britaine under the Conquests of ye Romans, Saxons, Danes and Normans William Hall & William Beale (1611).
-
- Bilson C. J. Medieval Leicester Edgar Backus (1920).
-
- Baldwin D. King Richard’s grave in Leicester. Trans. Leicestershire Archaeol. and Hist. Soc. 60, 21–24 (1986).
-
- Strange A. The Grey Friars, Leicester. Ricardian 3, 3–7 (1975).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

