The transcription factor FoxO1 sustains expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 and survival of antiviral CD8(+) T cells during chronic infection
- PMID: 25464856
- PMCID: PMC4270830
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.013
The transcription factor FoxO1 sustains expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 and survival of antiviral CD8(+) T cells during chronic infection
Abstract
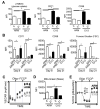
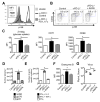
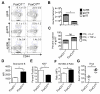
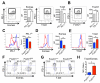
Protein kinase B (also known as AKT) and the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) are central regulators of T cell differentiation, proliferation, metabolism, and survival. Here, we show that during chronic murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection, activation of AKT and mTOR are impaired in antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), resulting in enhanced activity of the transcription factor FoxO1. Blockade of inhibitory receptor programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) in vivo increased mTOR activity in virus-specific CTLs, and its therapeutic effects were abrogated by the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin. FoxO1 functioned as a transcriptional activator of PD-1 that promoted the differentiation of terminally exhausted CTLs. Importantly, FoxO1-null CTLs failed to persist and control chronic viral infection. Collectively, this study shows that CTLs adapt to persistent infection through a positive feedback pathway (PD-1?FoxO1?PD-1) that functions to both desensitize virus-specific CTLs to antigen and support their survival during chronic viral infection.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439:682–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AI074699/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI074699/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32AI096718/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AR040072/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37AI066232/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI066232/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T325T32AI007019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32AI094791/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1-S10-RR-026526-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053495/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI102888/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR026526/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI096718/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007205/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI094791/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 AI066232/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI102888/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

