Inpatient mortality of HIV-infected adults in sub-Saharan Africa and possible interventions: a mixed methods review
- PMID: 25465206
- PMCID: PMC4265398
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-014-0627-9
Inpatient mortality of HIV-infected adults in sub-Saharan Africa and possible interventions: a mixed methods review
Abstract
Background: Despite the increased availability of anti-retroviral therapy, in-hospital HIV mortality remains high in sub-Saharan Africa. Reports from Senegal, Malawi, and Tanzania show rates of in-hospital, HIV-related mortality ranging from 24.2% to 44%. This mixed methods review explored the potential causes of preventable in-hospital mortality associated with HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa in the anti-retroviral era.
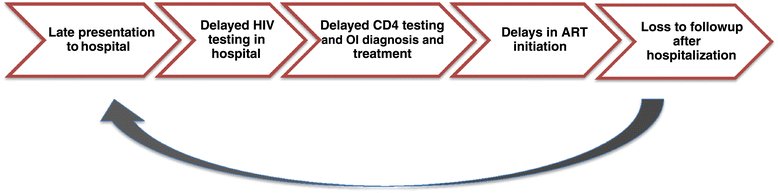
Results: Based on our experience as healthcare providers in Africa and a review of the literature we identified 5 health systems failures which may cause preventable in-hospital mortality, including: 1) late presentation of HIV cases, 2) low rates of in-hospital HIV testing, 3) poor laboratory capacity which limits CD4 T-cell testing and the diagnosis of opportunistic infections, 4) delay in initiation of anti-retroviral therapy in-hospital, and 5) problems associated with loss to follow-up upon discharge from hospital.
Conclusion: Our findings, together with the current available literature, should be used to develop practical interventions that can be implemented to reduce in-hospital mortality.
Figures
References
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS . Summary of the Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2002. pp. 1–35.
-
- Goosby E, Dybul M, Fauci AS, Fauci AA, Fu J, Walsh T, Needle R, Bouey P. The United States President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief: a story of partnerships and smart investments to turn the tide of the global AIDS pandemic. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012;60 Suppl 3:S51–S56. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31825ca721. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials