Global connectivity of hub residues in Oncoprotein structures encodes genetic factors dictating personalized drug response to targeted Cancer therapy
- PMID: 25465236
- PMCID: PMC4252896
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07294
Global connectivity of hub residues in Oncoprotein structures encodes genetic factors dictating personalized drug response to targeted Cancer therapy
Abstract
The efficacy and mechanisms of therapeutic action are largely described by atomic bonds and interactions local to drug binding sites. Here we introduce global connectivity analysis as a high-throughput computational assay of therapeutic action--inspired by the Google page rank algorithm that unearths most "globally connected" websites from the information-dense world wide web (WWW). We execute short timescale (30 ps) molecular dynamics simulations with high sampling frequency (0.01 ps), to identify amino acid residue hubs whose global connectivity dynamics are characteristic of the ligand or mutation associated with the target protein. We find that unexpected allosteric hubs--up to 20 Å from the ATP binding site, but within 5 Å of the phosphorylation site--encode the Gibbs free energy of inhibition (ΔG(inhibition)) for select protein kinase-targeted cancer therapeutics. We further find that clinically relevant somatic cancer mutations implicated in both drug resistance and personalized drug sensitivity can be predicted in a high-throughput fashion. Our results establish global connectivity analysis as a potent assay of protein functional modulation. This sets the stage for unearthing disease-causal exome mutations and motivates forecast of clinical drug response on a patient-by-patient basis. We suggest incorporation of structure-guided genetic inference assays into pharmaceutical and healthcare Oncology workflows.
Figures
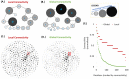

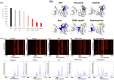


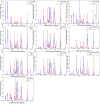

References
-
- Ringe D. & Petsko G. How Enzymes Work. Science 320, 1428–29 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Gilson M. K. & Zhou H.-X. Calculation of protein-ligand binding affinities. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 36, 21–42 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ciulli A., Williams G., Smith A. G., Blundell T. L. & Abell C. Probing Hot Spots at Protein-Ligand Binding Sites: A Fragment-Based Approach Using Biophysical Methods. J. Med. Chem. 49, 4992–5000 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Huang D., Lafleur K., Nevado C. & Caflisch A. Kinase selectivity potential for inhibitors targeting the ATP binding site: a network analysis. Bioinformatics 26, 198–204 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

