Mitochondrial anti-oxidant protects IEX-1 deficient mice from organ damage during endotoxemia
- PMID: 25466275
- PMCID: PMC4394602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.10.019
Mitochondrial anti-oxidant protects IEX-1 deficient mice from organ damage during endotoxemia
Abstract
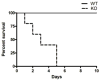
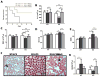
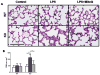
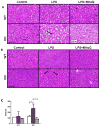
Sepsis, a leading cause of mortality in intensive care units worldwide, is often a result of overactive and systemic inflammation following serious infections. We found that mice lacking immediate early responsive gene X-1 (IEX-1) were prone to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -induced endotoxemia. A nonlethal dose of LPS provoked numerous aberrations in IEX-1 knockout (KO) mice including pancytopenia, increased serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and lung neutrophilia, concurrent with liver and kidney damage, followed by death. Given these results, in conjunction with a proven role for IEX-1 in the regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis during stress, we pre-treated IEX-1 KO mice with Mitoquinone (MitoQ), a mitochondrion-based antioxidant prior to LPS injection. The treatment significantly reduced ROS formation in circulatory cells and protected against pancytopenia and multiple organ failure, drastically increasing the survival rate of IEX-1 KO mice challenged by this low dose of LPS. This study confirms significant contribution of mitochondrial ROS to the etiology of sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest. This work is supported by the National Institutes of Health Grants CA158756, AI089779, and DA028378 to M.X.W. H.R. designed and performed the research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. M.X.W. has designed and supervised research and wrote the manuscript. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitoquinone restores platelet production in irradiation-induced thrombocytopenia.Platelets. 2015;26(5):459-66. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2014.935315. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Platelets. 2015. PMID: 25025394 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ protects against organ damage in a lipopolysaccharide-peptidoglycan model of sepsis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2008 Dec 1;45(11):1559-65. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.09.003. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008. PMID: 18845241
-
Pretreatment with Rho-kinase inhibitor ameliorates lethal endotoxemia-induced liver injury by improving mitochondrial function.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:125-130. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.036. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27588912
-
Mitochondria-Targeted Drugs.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2019;12(3):202-214. doi: 10.2174/1874467212666181127151059. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30479224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress in sepsis: Pathophysiological implications justifying antioxidant co-therapy.Burns. 2017 May;43(3):471-485. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2016.09.023. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Burns. 2017. PMID: 28034666 Review.
Cited by
-
Nicotinamide mononucleotide as a therapeutic agent to alleviate multi-organ failure in sepsis.J Transl Med. 2023 Dec 6;21(1):883. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04767-3. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38057866 Free PMC article.
-
Aged kidney: can we protect it? Autophagy, mitochondria and mechanisms of ischemic preconditioning.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(11):1291-1309. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1482149. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 29963970 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as major effectors of antimicrobial immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2020 May 28;16(5):e1008470. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008470. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32463825 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Emerging Potential of Immediate Early Response Gene X-1 in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Nov 6;7(21):e009261. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009261. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 30373431 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Interact With NLRP3 Inflammasomes and Are Involved in the Inflammation of Sepsis: From Mechanism to Treatment of Progression.Front Physiol. 2020 Nov 25;11:571810. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.571810. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33324236 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nimah M, Brilli RJ. Coagulation dysfunction in sepsis and multiple organ system failure. Crit Care Clin. 2003 Jul;19(3):441–58. - PubMed
-
- Martins PS, Kallas EG, Neto MC, Dalboni MA, Blecher S, Salomao R. Upregulation of reactive oxygen species generation and phagocytosis, and increased apoptosis in human neutrophils during severe sepsis and septic shock. Shock. 2003 Sep;20(3):208–12. - PubMed
-
- Combadiere C, El BJ, Pedruzzi E, Hakim J, Perianin A. Stimulation of the human neutrophil respiratory burst by formyl peptides is primed by a protein kinase inhibitor, staurosporine. Blood. 1993 Nov 1;82(9):2890–8. - PubMed
-
- Hurtado-Nedelec M, Makni-Maalej K, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Dang PM, El-Benna J. Assessment of priming of the human neutrophil respiratory burst. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1124:405–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

