Post-translational modifications of tubulin: pathways to functional diversity of microtubules
- PMID: 25468068
- PMCID: PMC4344850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.10.004
Post-translational modifications of tubulin: pathways to functional diversity of microtubules
Abstract
Tubulin and microtubules are subject to a remarkable number of post-translational modifications. Understanding the roles these modifications play in determining the functions and properties of microtubules has presented a major challenge that is only now being met. Many of these modifications are found concurrently, leading to considerable diversity in cellular microtubules, which varies with development, differentiation, cell compartment, and cell cycle. We now know that post-translational modifications of tubulin affect, not only the dynamics of the microtubules, but also their organization and interaction with other cellular components. Many early suggestions of how post-translational modifications affect microtubules have been replaced with new ideas and even new modifications as our understanding of cellular microtubule diversity comes into focus.
Keywords: acetylation; detyrosination; microtubule; polyamination; polyglutamylation; tubulin.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


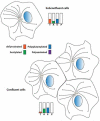

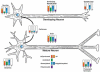
References
-
- Barra HS, et al. A soluble preparation from rat brain that incorporates into its own proteins ( 14 C)arginine by a ribonuclease-sensitive system and ( 14 C)tyrosine by a ribonuclease-insensitive system. J Neurochem. 1973;20:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Janke C, Bulinski JC. Post-translational regulation of the microtubule cytoskeleton: mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:773–786. - PubMed
-
- Janke C, Kneussel M. Tubulin post-translational modifications: encoding functions on the neuronal microtubule cytoskeleton. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:362–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

