Intrinsic islet heterogeneity and gap junction coupling determine spatiotemporal Ca²⁺ wave dynamics
- PMID: 25468351
- PMCID: PMC4255172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.10.048
Intrinsic islet heterogeneity and gap junction coupling determine spatiotemporal Ca²⁺ wave dynamics
Abstract
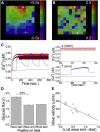
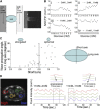
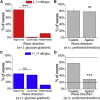
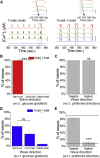
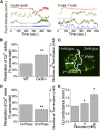
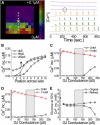
Insulin is released from the islets of Langerhans in discrete pulses that are linked to synchronized oscillations of intracellular free calcium ([Ca(2+)]i). Associated with each synchronized oscillation is a propagating calcium wave mediated by Connexin36 (Cx36) gap junctions. A computational islet model predicted that waves emerge due to heterogeneity in β-cell function throughout the islet. To test this, we applied defined patterns of glucose stimulation across the islet using a microfluidic device and measured how these perturbations affect calcium wave propagation. We further investigated how gap junction coupling regulates spatiotemporal [Ca(2+)]i dynamics in the face of heterogeneous glucose stimulation. Calcium waves were found to originate in regions of the islet having elevated excitability, and this heterogeneity is an intrinsic property of islet β-cells. The extent of [Ca(2+)]i elevation across the islet in the presence of heterogeneity is gap-junction dependent, which reveals a glucose dependence of gap junction coupling. To better describe these observations, we had to modify the computational islet model to consider the electrochemical gradient between neighboring β-cells. These results reveal how the spatiotemporal [Ca(2+)]i dynamics of the islet depend on β-cell heterogeneity and cell-cell coupling, and are important for understanding the regulation of coordinated insulin release across the islet.
Copyright © 2014 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Halban P.A., Wollheim C.B., Mintz D.H. The possible importance of contact between pancreatic islet cells for the control of insulin release. Endocrinology. 1982;111:86–94. - PubMed
-
- Ravier M.A., Güldenagel M., Meda P. Loss of connexin36 channels alters β-cell coupling, islet synchronization of glucose-induced Ca2+ and insulin oscillations, and basal insulin release. Diabetes. 2005;54:1798–1807. - PubMed
-
- Konstantinova I., Nikolova G., Lammert E. EphA-Ephrin-A-mediated β cell communication regulates insulin secretion from pancreatic islets. Cell. 2007;129:359–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK053434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK085145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD15052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK085145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK046409/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD016216/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD015052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK085145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025649/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- EY08126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK46409/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD010681/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM072048/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR026828/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

