Influence of kidney function on risk of supratherapeutic international normalized ratio-related hemorrhage in warfarin users: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 25468385
- PMCID: PMC4414676
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.11.004
Influence of kidney function on risk of supratherapeutic international normalized ratio-related hemorrhage in warfarin users: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Anticoagulation management is difficult in chronic kidney disease, with frequent supratherapeutic international normalized ratios (INRs ≥ 4) increasing hemorrhagic risk. We evaluated whether the interaction of INR and lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) increases hemorrhage risk and whether patients with lower eGFRs experience slower anticoagulation reversal.
Study design: Prospective cohort study.
Setting & participants: Warfarin pharmacogenetics cohort (1,273 long-term warfarin users); warfarin reversal cohort (74 warfarin users admitted with INRs ≥ 4).
Predictor: eGFR, INR as time-dependent covariate, and their interaction in the pharmacogenetics cohort; eGFR in the reversal cohort.
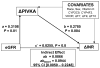
Outcomes & measurements: In the pharmacogenetics cohort, hemorrhagic (serious, life-threatening, and fatal bleeding) risk was assessed using proportional hazards regression. In the reversal cohort, anticoagulation reversal was assessed from changes in INR, warfarin and metabolite concentrations, clotting factors (II, VII, IX, and X), and PIVKA-II (protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II) levels at presentation and after reversal, using linear regression and path analysis.
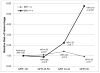
Results: In the pharmacogenetics cohort, 454 (35.7%) had eGFRs < 60 mL/min/1.73 m(2). There were 137 hemorrhages in 119 patients over 1,802 person-years of follow-up (incidence rate, 7.6 [95% CI, 6.4-8.9]/100 person-years). Patients with lower eGFRs had a higher frequency of INR ≥ 4 (P<0.001). Risk of hemorrhage was affected significantly by eGFR-INR interaction. At INR<4, there was no difference in hemorrhage risk by eGFR (all P ≥ 0.4). At INR≥4, patients with eGFRs of 30 to 44 and < 30 mL/min/1.73 m(2) had 2.2-fold (95% CI, 0.8-6.1; P=0.1) and 5.8-fold (95% CI, 2.9-11.4; P<0.001) higher hemorrhage risks, respectively, versus those with eGFRs ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m(2). In the reversal cohort, 35 (47%) had eGFRs < 45 mL/min/1.73 m(2). Patients with eGFRs < 45 mL/min/1.73 m(2) experienced slower anticoagulation reversal as assessed by INR (P=0.04) and PIVKA-II level (P=0.008) than those with eGFRs ≥ 45 mL/min/1.73 m(2).
Limitations: Limited sample size in the reversal cohort, unavailability of antibiotic use and urine albumin data.
Conclusions: Patients with lower eGFRs have differentially higher hemorrhage risk at INR ≥ 4. Moreover, because the INR reversal rate is slower, hemorrhage risk is prolonged.
Keywords: Kidney function; adverse event; chronic kidney disease (CKD); hemorrhage; pharmacokinetics; reversal of anticoagulation; supra-therapeutic international normalized ratio (INR); warfarin.
Copyright © 2015 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Wittkowsky AK, Devine EB. Frequency and causes of overanticoagulation and underanticoagulation in patients treated with warfarin. Pharmacotherapy. 2004 Oct;24(10):1311–1316. - PubMed
-
- Hylek EM, Chang YC, Skates SJ, Hughes RA, Singer DE. Prospective study of the outcomes of ambulatory patients with excessive warfarin anticoagulation. Arch Intern Med. 2000 Jun 12;160(11):1612–1617. - PubMed
-
- Hylek EM, Go AS, Chang Y, et al. Effect of intensity of oral anticoagulation on stroke severity and mortality in atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2003 Sep 11;349(11):1019–1026. - PubMed
-
- Budnitz DS, Lovegrove MC, Shehab N, Richards CL. Emergency hospitalizations for adverse drug events in older Americans. N Engl J Med. 2011 Nov 24;365(21):2002–2012. - PubMed
-
- Nolin TD, Naud J, Leblond FA, Pichette V. Emerging evidence of the impact of kidney disease on drug metabolism and transport. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2008 Jun;83(6):898–903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

