Epigenetic modifications are associated with inter-species gene expression variation in primates
- PMID: 25468404
- PMCID: PMC4290387
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-014-0547-3
Epigenetic modifications are associated with inter-species gene expression variation in primates
Abstract
Background: Changes in gene regulation have long been thought to play an important role in evolution and speciation, especially in primates. Over the past decade, comparative genomic studies have revealed extensive inter-species differences in gene expression levels, yet we know much less about the extent to which regulatory mechanisms differ between species.
Results: To begin addressing this gap, we perform a comparative epigenetic study in primate lymphoblastoid cell lines, to query the contribution of RNA polymerase II and four histone modifications, H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me3, to inter-species variation in gene expression levels. We find that inter-species differences in mark enrichment near transcription start sites are significantly more often associated with inter-species differences in the corresponding gene expression level than expected by chance alone. Interestingly, we also find that first-order interactions among the five marks, as well as chromatin states, do not markedly contribute to the degree of association between the marks and inter-species variation in gene expression levels, suggesting that the marginal effects of the five marks dominate this contribution.
Conclusions: Our observations suggest that epigenetic modifications are substantially associated with changes in gene expression levels among primates and may represent important molecular mechanisms in primate evolution.
Figures
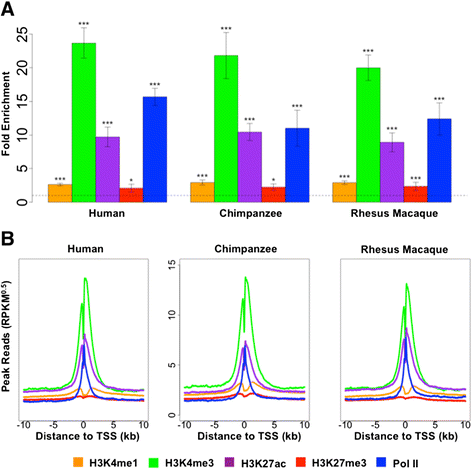
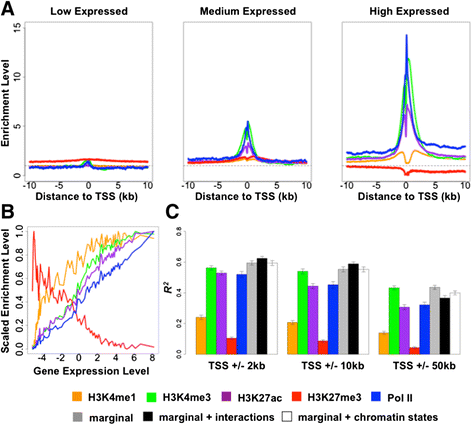



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- RR016483/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR00168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR014491/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K26 RR000168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM077959/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM084996/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U42 RR015087/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM077959/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR015087/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR016483/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR014491/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM084996/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

