Heterotopic pancreatic tissue in the gastric cardia: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 25469051
- PMCID: PMC4248226
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16779
Heterotopic pancreatic tissue in the gastric cardia: a case report and literature review
Abstract
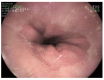
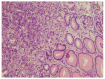
The heterotopic pancreas, which is usually described as an untypical presence of pancreatic tissue without any anatomic or vascular continuity with the pancreas, is relatively rare. Clinical manifestations may include bleeding, inflammation, pain and obstruction; however, in most cases it remains silent and is diagnosed during autopsy. Here, we report a case of ectopic pancreatic lesion located in the gastric cardia. The patient was a 73-year-old woman who had a history (over four months) of chronic epigastric pain accompanied by heartburn. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy revealed inflammatory changes throughout the stomach and lower esophagus, as well as a flat polypoid mass with benign features located in the gastric cardia, approx. 10 mm below the "Z" line, measuring approx. 7 mm in diameter. Endoscopic biopsy forceps were used to remove the lesion. Histological examination of the lesion revealed the presence of heterotopic pancreatic tissue in the gastric mucosa. On the basis of the presented case, we suggest that pancreatic ectopia should be a part of differential diagnosis, not only when dealing with submucosal gastric lesions, but also with those that are small, flat and/or untypically located.
Keywords: Ectopia; Epigastric pain; Gastric cardia; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Pancreatic tissue.
Figures
References
-
- Agale SV, Agale VG, Zode RR, Grover S, Joshi S. Heterotopic pancreas involving stomach and duodenum. J Assoc Physicians India. 2009;57:653–654. - PubMed
-
- Cullen JJ, Weydert C, Hinkhouse MM, Ritchie J, Domann FE, Spitz D, Oberley LW. The role of manganese superoxide dismutase in the growth of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1297–1303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

