Dentin reactions to caries are misinterpreted by histological "gold standards"
- PMID: 25469227
- PMCID: PMC4240241
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.3-13.v1
Dentin reactions to caries are misinterpreted by histological "gold standards"
Abstract
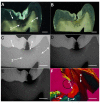
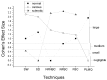
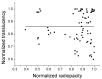
Dentin reactions to caries, crucial for pathogenesis and for the determination of the severity of caries lesions, are believed to be reasonably detected by stereomicroscopy (SM) and polarized light microscopy in quinoline (PLMQ), but accuracies are not available. Here, stereomicroscopy of wet (SW) and dry (SD) ground sections of natural occlusal caries lesions resulted in moderate (0.7, for normal dentin) and low accuracies (< 0.6, for carious and sclerotic dentin) as validated by contrast-corrected microradiography. Accuracies of PLMQ were moderate for both normal (0.71) and carious dentin (0.71). The hypothesis that detection of dentin reactions by SM and PLMQ would be influenced by the contrast quality of micrographic images was rejected. Dentin reactions were scored by SW, SD, PLMQ, and three types of microradiographic images with varying contrast qualities and each technique was compared against the one that resulted in the highest number of scores for each dentin reaction. Large differences resulted, mainly related to the detection of sclerotic dentin by both SW and SD, and normal and carious dentin by PLMQ. It is concluded that contrast-corrected microradiography should be preferred as the gold standard and SM and PLMQ should be avoided, but the relationship of PLMQ with dentin mineralization deserves further investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation between ICDAS and histology: Differences between stereomicroscopy and microradiography with contrast solution as histological techniques.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 25;12(8):e0183432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183432. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28841688 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the color of carious dentin with varying lesion activity, and bacterial detection.J Dent. 2008 Feb;36(2):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2007.11.012. Epub 2008 Jan 8. J Dent. 2008. PMID: 18191886
-
The relationship between the color of carious dentin stained with a caries detector dye and bacterial infection.Oper Dent. 2005 Jan-Feb;30(1):83-9. Oper Dent. 2005. PMID: 15765962
-
Morphological analysis and chemical content of natural dentin carious lesion zones.Ann Anat. 2003 Oct;185(5):419-24. doi: 10.1016/S0940-9602(03)80099-7. Ann Anat. 2003. PMID: 14575268
-
Dentin bonding: effect of degree of mineralization and acid etching time.Oper Dent. 2003 Jul-Aug;28(4):429-39. Oper Dent. 2003. PMID: 12877429
Cited by
-
Correlation between ICDAS and histology: Differences between stereomicroscopy and microradiography with contrast solution as histological techniques.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 25;12(8):e0183432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183432. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28841688 Free PMC article.
-
Natural enamel caries, dentine reactions, dentinal fluid and biofilm.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 26;9(1):2841. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38684-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30808878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) X-ray attenuation databases. Reference Source
-
- Elliott JC: Structure, crystal chemistry and density of enamel apatites. In Dental Enamel. Ciba Found Symp.Chadwick D, Cardew G, editors. Chichester: Wiley,1997; 205:54–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

