Arterial stiffness and chronic kidney disease: lessons from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study
- PMID: 25470015
- PMCID: PMC5180446
- DOI: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000086
Arterial stiffness and chronic kidney disease: lessons from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study
Abstract
Purpose of review: The purpose of this review is to highlight what the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study has taught us regarding arterial stiffness in chronic kidney disease. The CRIC study began in mid-2003 and enrolled more than 3900 people with chronic kidney disease.
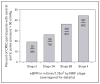
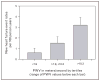
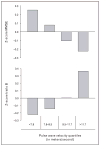
Recent findings: The recent findings from the CRIC study are covered in 10 lessons. Within the CRIC study, we enrolled about 2800 participants who underwent a pulse wave velocity measurement. At the time of initial funding, very little was known about the role of arterial stiffness in chronic, nondialyzed, kidney disease. The lessons span the gamut from simple correlations to measures such as central arterial pressure profiles and reproducibility of pulse wave velocity measurements between operators, to relationships of pulse wave velocity to kidney function, protein excretion, cardiovascular disease prevalence, and incident cardiovascular events such as heart failure.
Summary: The implications from these lessons are that pulse wave velocity is a robust, reproducible measure of arterial stiffness which adds important information to standard clinical assessments such as SBP and DBP in a population with chronic kidney disease, a disorder with high likelihood of progressive kidney function loss, and a substantial predisposition to cardiovascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The author acknowledges grant support from the NIH, as outlined above.
Figures



References
-
- Shulman NB, Ford CE, Hall WD, et al. Prognostic value of serum creatinine and effect of treatment of hypertension on renal function. Results from the hypertension detection and follow-up program. The Hypertension Detection and Follow-up Program Cooperative Group. Hypertension. 1989;13:I80–I93. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Levey AS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. J Am Med Assoc. 2007;298:2038–2047. - PubMed
-
- Rostand SG, Brown G, Kirk KA, et al. Renal insufficiency in treated essential hypertension. Clin Nephrol. 1989;320:684–688. - PubMed
-
- Parsa A, Kao WH, Xie D, et al. APOL1 risk variants, race, and progression of chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2183–2196. This study shows a significant role for the presence of the G1 and G2 risk alleles in patients of African descent with CKD. They progress to worsened levels of renal function, whether or not diabetes is present, more rapidly than African descent patients without the risk alleles, or whites. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067390/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR-000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

