Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 Inhibits Oxidized LDL-induced differentiation of RAW264.7 murine macrophage cell line into dendritic like cells
- PMID: 25471687
- PMCID: PMC4274730
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-014-0054-z
Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 Inhibits Oxidized LDL-induced differentiation of RAW264.7 murine macrophage cell line into dendritic like cells
Abstract
Background: Nur77 is an orphan nuclear receptor expressed in human atheroma. In vascular cells in vitro, Nur77 expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, such as oxidized LDL (oxLDL).
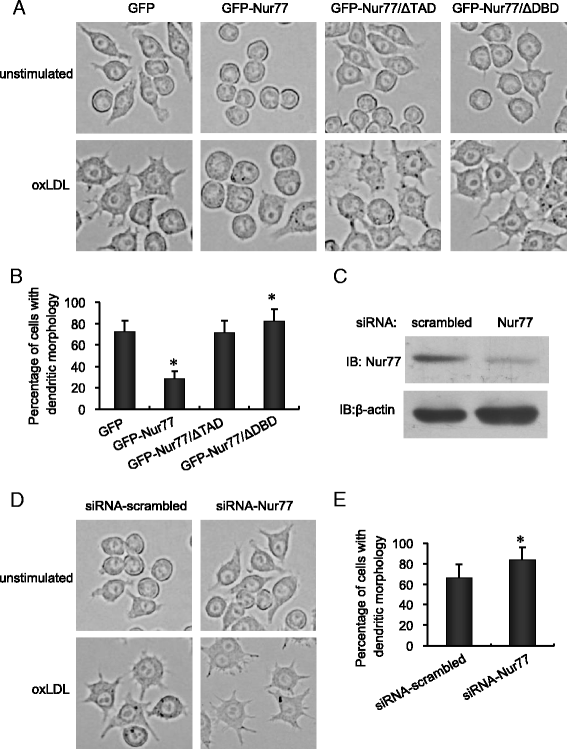
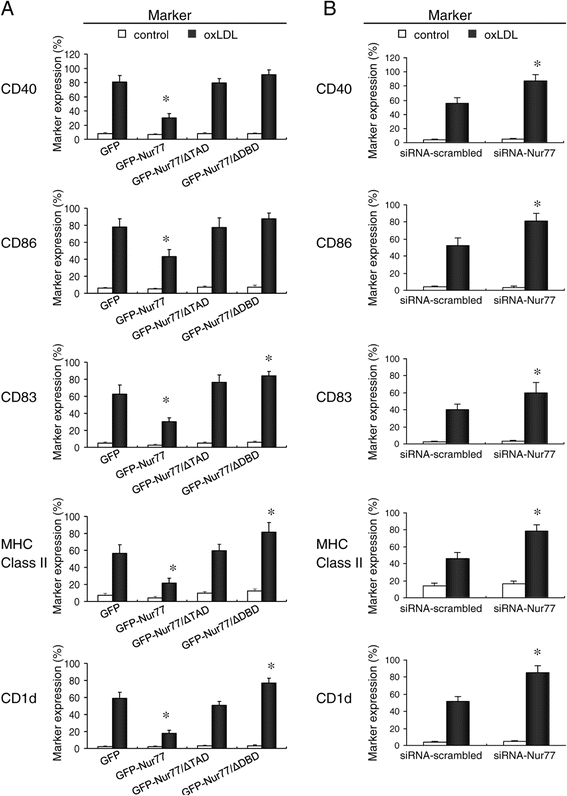
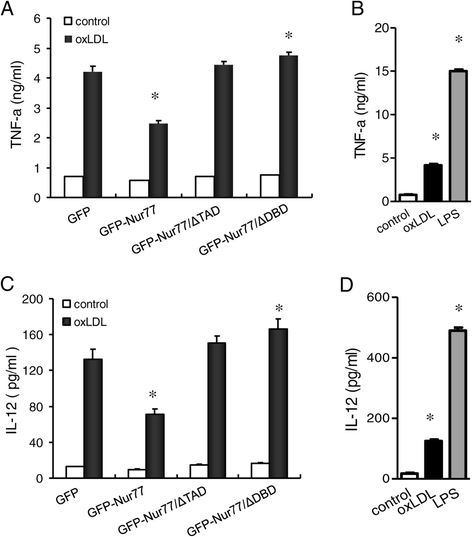
Methods: We analyze the role of Nur77 in the oxLDL-induced differentiation of macrophages into dendritic cells (DC). The murine RAW264.7 macrophage cell line was stably transfected with expression plasmids encoding either GFP or GFP fusions with either full-length Nur77 (GFP-Nur77), Nur77 lacking the DNA binding domain (GFP-Nur77-ΔDBD) or Nur77 lacking the transactivation domain (GFP-Nur77-ΔTAD).
Results: GFP-Nur77 overexpression significantly suppressed the effect of oxLDL treatment on DC morphologic changes, expression of DC maturation markers, endocytic activity, allogeneic activation of T cell proliferation, and the activity and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Analysis of GFP-Nur77-ΔTAD and GFP-Nur77-ΔDBD indicated that the Nur77 DNA binding and transactivation domains were both required for this effect. GFP-Nur77-ΔDBD consistently had the opposite effect to GFP-Nur77, increasing DC-type differentiation in all assays. Interestingly, GFP-Nur77-ΔDBD protein was cytosolic, whereas GFP-Nur77 and GFP-Nur77-ΔTAD were both nuclear.
Conclusions: These data show that GFP-Nur77 inhibited differentiation of oxLDL-treated macrophages into DC. The effects of Nur77 on the macrophage phenotype may involve changes in its subcellular distribution.
Figures


References
-
- Dahl TB, Arne Y, Mona S, Erik O, Arve D, Annika M, Damås JK, Tunheim SH, Thor U, Camilla S, Bjørn B, Serena T, Lars G, Frøland SS, Kirsten K-S, David R, Pål A, Bente H. Increased Expression of Visfatin in Macrophages of Human Unstable Carotid and Coronary Atherosclerosis: Possible Role in Inflammation and Plaque Destabilization. Circulation. 2007;115(8):972–980. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.665893. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

