PET/CT imaging reveals a therapeutic response to oxazolidinones in macaques and humans with tuberculosis
- PMID: 25473035
- PMCID: PMC6413515
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009500
PET/CT imaging reveals a therapeutic response to oxazolidinones in macaques and humans with tuberculosis
Abstract
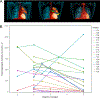
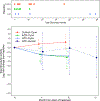
Oxazolidinone antibiotics such as linezolid have shown significant therapeutic effects in patients with extensively drug-resistant (XDR) tuberculosis (TB) despite modest effects in rodents and no demonstrable early bactericidal activity in human phase 2 trials. We show that monotherapy with either linezolid or AZD5847, a second-generation oxazolidinone, reduced bacterial load at necropsy in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected cynomolgus macaques with active TB. This effect coincided with a decline in 2-deoxy-2-[(18)F]-fluoro-d-glucose positron emission tomography (FDG PET) imaging avidity in the lungs of these animals and with reductions in pulmonary pathology measured by serial computed tomography (CT) scans over 2 months of monotherapy. In a parallel phase 2 clinical study of linezolid in patients infected with XDR-TB, we also collected PET/CT imaging data from subjects receiving linezolid that had been added to their failing treatment regimens. Quantitative comparisons of PET/CT imaging changes in these human subjects were similar in magnitude to those observed in macaques, demonstrating that the therapeutic effect of these oxazolidinones can be reproduced in this model of experimental chemotherapy. PET/CT imaging may be useful as an early quantitative measure of drug efficacy against TB in human patients.
Copyright © 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

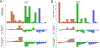

References
-
- Zumla A, George A, Sharma V, Herbert N, Baroness Masham of I, WHO’s 2013 global report on tuberculosis: successes, threats, and opportunities. Lancet 382, 1765–1767 (2013). - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, in Treatment of Tuberculosis: Guidelines. 4th edition. (Geneva, 2010). - PubMed
-
- Christian KA, Ijaz K, Dowell SF, Chow CC, Chitale RA, Bresee JS, Mintz E, Pallansch MA, Wassilak S, McCray E, Arthur RR, What we are watching--five top global infectious disease threats, 2012: a perspective from CDC’s Global Disease Detection Operations Center. Emerging health threats journal 6, 20632 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franzblau SG, DeGroote MA, Cho SH, Andries K, Nuermberger E, Orme IM, Mdluli K, Angulo-Barturen I, Dick T, Dartois V, Lenaerts AJ, Comprehensive analysis of methods used for the evaluation of compounds against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 92, 453–488 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

