In vivo effects of adipose-derived stem cells in inducing neuronal regeneration in Sprague-Dawley rats undergoing nerve defect bridged with polycaprolactone nanotubes
- PMID: 25473208
- PMCID: PMC4248004
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S3.S183
In vivo effects of adipose-derived stem cells in inducing neuronal regeneration in Sprague-Dawley rats undergoing nerve defect bridged with polycaprolactone nanotubes
Abstract
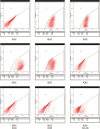
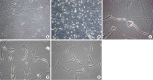
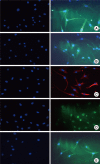
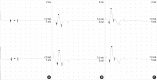
There have been many attempts for regeneration of peripheral nerve injury. In this study, we examined the in vivo effects of non-differentiated and neuronal differentiated adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) in inducing the neuronal regeneration in the Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats undergoing nerve defect bridged with the PCL nanotubes. Then, we performed immunohistochemical and histopathologic examinations, as well as the electromyography, in three groups: the control group (14 sciatic nerves transplanted with the PCL nanotube scaffold), the experimental group I (14 sciatic nerves with the non-differentiated ADSCs at a density of 7×10(5) cells/0.1 mL) and the experimental group II (14 sciatic nerves with the neuronal differentiated ADSCs at 7×10(5) cells/0.1 mL). Six weeks postoperatively, the degree of the neuronal induction and that of immunoreactivity to nestin, MAP-2 and GFAP was significantly higher in the experimental group I and II as compared with the control group. In addition, the nerve conduction velocity (NCV) was significantly higher in the experimental group I and II as compared with the control group (P=0.021 and P=0.020, respectively). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in the NCV between the two experimental groups (P>0.05). Thus, our results will contribute to treating patients with peripheral nerve defects using PCL nanotubes with ADSCs.
Keywords: Adipose Tissue; Matrix Attachment Regions; Nanotubes; Peripheral Nerves; Polycaprolactone; Regeneration; Stem Cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Martínez de Albornoz P, Delgado PJ, Forriol F, Maffulli N. Non-surgical therapies for peripheral nerve injury. Br Med Bull. 2011;100:73–100. - PubMed
-
- Lin MY, Manzano G, Gupta R. Nerve allografts and conduits in peripheral nerve repair. Hand Clin. 2013;29:331–348. - PubMed
-
- Kingham PJ, Kalbermatten DF, Mahay D, Armstrong SJ, Wiberg M, Terenghi G. Adipose-derived stem cells differentiate into a Schwann cell phenotype and promote neurite outgrowth in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2007;207:267–274. - PubMed
-
- Papalia I, Raimondo S, Ronchi G, Magaudda L, Giacobini-Robecchi MG, Geuna S. Repairing nerve gaps by vein conduits filled with lipoaspirate-derived entire adipose tissue hinders nerve regeneration. Ann Anat. 2013;195:225–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

