Critical role of NF-κB in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 25473891
- PMCID: PMC4294354
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2624
Critical role of NF-κB in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the deadliest cancers, and in spite of intense efforts there are limited therapeutic options for patients with PDAC. PDACs harbor a high frequency of Kras mutations and other driver mutations that lead to altered signaling pathways and contribute to therapeutic resistance. Importantly, constitutive activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) is frequently observed in PDAC. An increasing body of evidence suggests that both classical and non-classical NF-κB pathways play a crucial role in PDAC development and progression. In this review, we update the most recent advances regarding different aspects of NF-κB involvement in PDAC development and progression, emphasizing its potential as a therapeutic target and the need to discover pathway-specific cytosolic NF-κB regulators which could be used to design novel therapeutic strategies for PDAC.
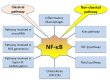
Figures

References
-
- Sen R, Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986;46:705–16. - PubMed
-
- Gilmore TD. Introduction to NF-κB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene. 2006;25:6680–84. - PubMed
-
- Lenardo MJ, Pierce JW, Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987;236:1573–77. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal B, Shishodiab S. Molecular targets of dietary agents for prevention and therapy of cancer. Science Direct. 2006;71:1397–421. - PubMed
-
- Lu T, Sathe SS, Swiatkowski SM, Hampole CV, Stark GR. Secretion of cytokines and growth factors as a general cause of constitutive NF-κB activation in cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23:2136–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

