Evaluation of azacitidine and entinostat as sensitization agents to cytotoxic chemotherapy in preclinical models of non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 25474141
- PMCID: PMC4381578
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2695
Evaluation of azacitidine and entinostat as sensitization agents to cytotoxic chemotherapy in preclinical models of non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
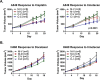
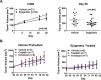
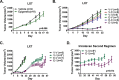
Recent clinical data in lung cancer suggests that epigenetically targeted therapy may selectively enhance chemotherapeutic sensitivity. There have been few if any studies rigorously evaluating this hypothesized priming effect. Here we describe a series of investigations testing whether epigenetic priming with azacitidine and entinostat increases sensitivity of NSCLC to cytotoxic agents. We noted no differences in chemosensitivity following treatment with epigenetic therapy in in vitro assays of viability and colony growth. Using cell line and patient derived xenograft (PDX) models, we also observed no change in responsiveness to cisplatin in vivo. In select models, we noted differential responses to irinotecan treatment in vivo. In vitro epigenetic therapy prior to tumor implantation abrogated response of H460 xenografts to irinotecan. Conversely, in vitro epigenetic therapy appeared to sensitize A549 xenografts (tumor growth inhibition 51%, vs. 22% in mock-pretreated control). In vivo epigenetic therapy enhanced the response of adenocarcinoma PDX to irinotecan. Taken together, these data do not support broadly applicable epigenetic priming in NSCLC. Priming effects may be context-specific, dependent on both tumor and host factors. Further preclinical study is necessary to determine whether, and in which contexts, priming with epigenetic therapy has potential to enhance chemotherapeutic efficacy in NSCLC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
SBB has research support from MDxHealth, and holds a patent licensed to MDxHealth. These arrangements are managed by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. CMR has been a paid consultant regarding cancer drug development for AbbVie, Aveo, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Janne PA. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2008;14:2895–2899. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Martins RG, Spigel D, Grunberg SM, Spira A, Janne PA, Joshi VA, McCollum D, Evans TL, Muzikansky A, Kuhlmann GL, Han M, Goldberg JS, et al. First-line gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring somatic EGFR mutations. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26:2442–2449. - PubMed
-
- Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, Ueno T, Takashima J, Nakajima T, Yatabe Y, Takeuchi K, Hamada T, Haruta H, Ishikawa Y, Kimura H, Mitsudomi T, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. NEnglJMed. 2010;363:1734–1739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

