Prevalence and determinants of tobacco use in India: evidence from recent Global Adult Tobacco Survey data
- PMID: 25474196
- PMCID: PMC4256395
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114073
Prevalence and determinants of tobacco use in India: evidence from recent Global Adult Tobacco Survey data
Abstract
Background: Tobacco use in India is characterized by a high prevalence of smoking and smokeless tobacco use, with dual use also contributing a noticeable proportion. In the context of such a high burden of tobacco use, this study examines the regional variations, and socioeconomic, demographic and other correlates of smoking, smokeless tobacco and dual use of tobacco in India.
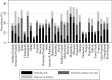
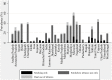
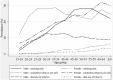
Methods and findings: We analyzed a cross sectional, nationally representative sample of individuals from the Global Adult Tobacco Survey in India (2009-10), which covered 69,296 individuals aged 15 years and above. The current tobacco use in three forms, namely, smoking only, smokeless tobacco use only, and both smoking and smokeless tobacco use were considered as outcomes in this study. Descriptive statistics, cross tabulations and multinomial logistic regression analysis were adopted as analytical tools. Smokeless tobacco use was the major form of tobacco use in India followed by smoking and dual tobacco use. Tobacco use was higher among males, the less educated, the poor, and the rural population in India. Respondents lacking knowledge of health hazards of tobacco had higher prevalence of tobacco use in each form. The prevalence of different forms of tobacco use varies significantly by states. The prevalence of tobacco use increases concomitantly with age among females. Middle-aged adult males had higher prevalence of tobacco use. Age, education and region were found to be significant determinants of all forms of tobacco use. Adults from the poor household had significantly higher risk of consuming smokeless tobacco. Lack of awareness about the selected hazards of tobacco significantly affects tobacco use.
Conclusions: There is an urgent need to curb the use of tobacco among the sub-groups of population with higher prevalence. Tobacco control policies in India should adopt a targeted, population-based approach to control and reduce tobacco consumption in the country.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rani M, Bonu S, Jha P, Nguyen SN, Jamjoum L (2003) Tobacco use in India: Prevalence and predictors of smoking and chewing in a national cross sectional household survey. Tob Control 12:e4 doi:10.1136/tc.12.4.e4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reddy KS, Arora M (2005) Global Youth Tobacco Survey (GYTS) – Delhi. Indian Pediatr 42:850–851. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2008) WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2008: The MPOWER package . Geneva : World Health Organization .
-
- Jha P, Jacob B, Gajalakshmi V, Gupta PC, Dhingra N, et al. (2008) A nationally representative case-control study of smoking and death in India. N Engl J Med 358(11):1137–1147. - PubMed
-
- Reddy KS, Gupta PC (2004) Report on tobacco control in India. New Delhi: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources