A meta-analysis of the effect of preoperative biliary stenting on patients with obstructive jaundice
- PMID: 25474436
- PMCID: PMC4616392
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000189
A meta-analysis of the effect of preoperative biliary stenting on patients with obstructive jaundice
Abstract
The goal of this study was to systematically review the effects of biliary stenting on postoperative morbidity and mortality of patients with obstructive jaundice. PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and other relevant databases were searched by computer and manually for published and unpublished studies on the impact of preoperative biliary drainage on patients with obstructive jaundice from 2000 to the present day. Two investigators independently selected the studies according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, extracted the data, and assessed the quality of the selected studies. Meta-analysis was performed to compare postoperative morbidity and mortality of patients between the drainage and nondrainage groups.Compared with the nondrainage group, the overall mortality, overall morbidity, infectious morbidity, incidence of wound infection, intra-abdominal abscess, pancreatic fistulas, bile leak, and delayed gastric emptying in the drainage group were not significantly different. Compared with the nondrainage group, the drainage group had a drainage time of <4 weeks with an increased overall morbidity by 7% to 23%; however, the overall morbidity of the drainage group with a drainage time >4 weeks was not significantly different. Compared with the nondrainage group, the overall mortality of the drainage group using metal stents and plastic stents as internal drainage devices was reduced by 0.5% to 6%, whereas that of the drainage group using plastic stent devices was not significantly different.In summary, preoperative drainage should be applied selectively. The drainage time should be >4 weeks, and metal stents should be used for internal drainage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


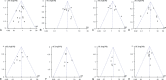


References
-
- Lai EC, Chu KM, Lo CY, et al. Surgery for malignant obstructive jaundice: analysis of mortality. Surgery 1992; 112:891–896. - PubMed
-
- Karsten T, Allema J, Reinders M, et al. Preoperative biliary drainage, colonisation of bile and postoperative complications in patients with tumours of the pancreatic head: a retrospective analysis of 241 consecutive patients. Eur J Surg 1996; 162:881–888. - PubMed
-
- Pešková M, Gürlich R. Preoperative biliary drainage before pancreatoduodenectomy in patients with obstructive jaundice. Eur Surg 2005; 37:331–335.
-
- Sewnath ME, Birjmohun RS, Rauws EA, et al. The effect of preoperative biliary drainage on postoperative complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Am Coll Surg 2001; 192:726–734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

