FTO: linking m6A demethylation to adipogenesis
- PMID: 25475057
- PMCID: PMC4650590
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2014.162
FTO: linking m6A demethylation to adipogenesis
Abstract
Polymorphism of the FTO gene encoding an N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) RNA demethylase was robustly associated with human obesity; however, the mechanism by which FTO affects metabolism, considering its emerging role in RNA modification, is still poorly understood. A new study published in Cell Research reports novel functions implicating FTO in the regulation of mRNA alternative splicing in the control of adipogenesis.
Figures
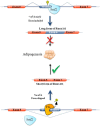
Comment on
-
FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis.Cell Res. 2014 Dec;24(12):1403-19. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.151. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 25412662 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

