DNA strand exchange and RecA homologs in meiosis
- PMID: 25475089
- PMCID: PMC4292170
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016659
DNA strand exchange and RecA homologs in meiosis
Abstract
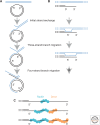
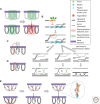
Homology search and DNA strand-exchange reactions are central to homologous recombination in meiosis. During meiosis, these processes are regulated such that the probability of choosing a homolog chromatid as recombination partner is enhanced relative to that of choosing a sister chromatid. This regulatory process occurs as homologous chromosomes pair in preparation for assembly of the synaptonemal complex. Two strand-exchange proteins, Rad51 and Dmc1, cooperate in regulated homology search and strand exchange in most organisms. Here, we summarize studies on the properties of these two proteins and their accessory factors. In addition, we review current models for the assembly of meiotic strand-exchange complexes and the possible mechanisms through which the interhomolog bias of recombination partner choice is achieved.
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Alexeev A, Mazin A, Kowalczykowski SC 2003. Rad54 protein possesses chromatin-remodeling activity stimulated by the Rad51–ssDNA nucleoprotein filament. Nat Struct Biol 10: 182–186. - PubMed
-
- Baumann P, Benson FE, West SC 1996. Human Rad51 protein promotes ATP-dependent homologous pairing and strand transfer reactions in vitro. Cell 87: 757–766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
