MicroRNAs: new players in IBD
- PMID: 25475103
- PMCID: PMC4345829
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307891
MicroRNAs: new players in IBD
Erratum in
-
MicroRNAs: new players in inflammatory bowel disease.Gut. 2015 Jun;64(6):1008. doi: 10.1136/gut.2014.307891corr1. Gut. 2015. PMID: 25957388 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
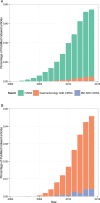
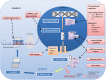
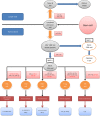
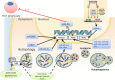
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs, 18-23 nucleotides long, which act as post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression. miRNAs are strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of many common diseases, including IBDs. This review aims to outline the history, biogenesis and regulation of miRNAs. The role of miRNAs in the development and regulation of the innate and adaptive immune system is discussed, with a particular focus on mechanisms pertinent to IBD and the potential translational applications.
Keywords: CELLULAR IMMUNOLOGY; CROHN'S DISEASE; INTESTINAL TRACT; T LYMPHOCYTES; ULCERATIVE COLITIS.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures

References
-
- Burisch J, Jess T, Martinato M, et al. . The burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Europe. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:322–37. - PubMed
-
- Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet 2011;12:861–74. - PubMed
-
- Xu W-D, Pan H-F, Li J-H, et al. . MicroRNA-21 with therapeutic potential in autoimmune diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2013;17:659–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
