In vivo flow mapping in complex vessel networks by single image correlation
- PMID: 25475129
- PMCID: PMC4256590
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07341
In vivo flow mapping in complex vessel networks by single image correlation
Abstract
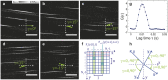
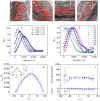
We describe a novel method (FLICS, FLow Image Correlation Spectroscopy) to extract flow speeds in complex vessel networks from a single raster-scanned optical xy-image, acquired in vivo by confocal or two-photon excitation microscopy. Fluorescent flowing objects produce diagonal lines in the raster-scanned image superimposed to static morphological details. The flow velocity is obtained by computing the Cross Correlation Function (CCF) of the intensity fluctuations detected in pairs of columns of the image. The analytical expression of the CCF has been derived by applying scanning fluorescence correlation concepts to drifting optically resolved objects and the theoretical framework has been validated in systems of increasing complexity. The power of the technique is revealed by its application to the intricate murine hepatic microcirculatory system where blood flow speed has been mapped simultaneously in several capillaries from a single xy-image and followed in time at high spatial and temporal resolution.
Figures


References
-
- Tuma R. F., Duran W. N. & Ley K. Microcirculation. Handbook of Physiology. Second Edition, Elsevier Science. (2008).
-
- Carmeliet P. et al. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 9, 653–660 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Jain R. K. et al. Molecular regulation of vessel maturation. Nat. Med. 9, 685–693 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Adams R. H. & Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8, 464–478 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Briers J. D. Laser Doppler, speckle and related techniques for blood perfusion mapping and imaging. Physiol. Meas. 22, R35–R66 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

