Serum uric acid level and the incidence of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean men: a 5-year follow-up study
- PMID: 25475199
- PMCID: PMC4263007
- DOI: 10.3961/jpmph.14.028
Serum uric acid level and the incidence of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean men: a 5-year follow-up study
Abstract
Objectives: Elevated serum uric acid (UA) has been known to be associated with the prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MetS). However, no prospective studies have examined whether serum UA levels are actually associated with the development of MetS. We performed a prospective study to evaluate the longitudinal effects of baseline serum UA levels on the development of MetS.
Methods: A MetS-free cohort of 14 906 healthy Korean men, who participated in a medical check-up program in 2005, was followed until 2010. MetS was defined according to the Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention. Cox proportional hazards models were performed.
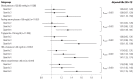
Results: During 52 466.1 person-years of follow-up, 2428 incident cases of MetS developed between 2006 and 2010. After adjusting for multiple covariates, the hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals) for incident MetS for the second, the third, and the fourth quartile to the first quartile of serum UA levels were 1.09 (0.92-1.29), 1.22 (1.04-1.44), and 1.48 (1.26-1.73), respectively (p for trend <0.001). These associations were also significant in the clinically relevant subgroup analyses.
Conclusions: Elevated serum UA levels were independently associated with future development of MetS in Korean men during the 5-year follow-up period.
Keywords: Cohort studies; Metabolic syndrome X; Uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest with the material presented in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prospective study of serum uric acid levels and incident metabolic syndrome in a Korean rural cohort.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Jul;241(1):271-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.04.797. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 25957887
-
Serum uric acid: A strong and independent predictor of metabolic syndrome after adjusting for body composition.Metabolism. 2016 Apr;65(4):432-40. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Metabolism. 2016. PMID: 26975535
-
Longitudinal increase in gamma-glutamyltransferase within the reference interval predicts metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean men.Metabolism. 2010 May;59(5):683-9. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.08.024. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Metabolism. 2010. PMID: 19922966
-
Does the Combination of Metabolic Syndrome and Low Fat-Free Mass Shorten an Individual's Disability-Free Life? A 12-Year Prospective Cohort Study of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES).Public Health Nurs. 2025 Mar-Apr;42(2):675-683. doi: 10.1111/phn.13494. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Public Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39603811 Review.
-
Association between metabolic syndrome and uric acid: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 1;12(1):18412. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22025-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36319728 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between baseline and changes in serum uric acid and incident metabolic syndrome: a nation-wide cohort study and updated meta-analysis.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2021 Jun 9;18(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12986-021-00584-x. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34108010 Free PMC article.
-
High-Fructose Diet-Induced Hyperuricemia Accompanying Metabolic Syndrome-Mechanisms and Dietary Therapy Proposals.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 17;20(4):3596. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043596. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Associations of Serum Uric Acid with Obesity-Related Acanthosis nigricans and Related Metabolic Indices.Int J Endocrinol. 2017;2017:5438157. doi: 10.1155/2017/5438157. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Int J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28367214 Free PMC article.
-
Can biomarkers be used to improve diagnosis and prediction of metabolic syndrome in childhood cancer survivors? A systematic review.Obes Rev. 2021 Nov;22(11):e13312. doi: 10.1111/obr.13312. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Obes Rev. 2021. PMID: 34258851 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Uric Acid and Metabolic Syndrome in Elderly Women.Open Med (Wars). 2018 May 9;13:172-177. doi: 10.1515/med-2018-0027. eCollection 2018. Open Med (Wars). 2018. PMID: 29756053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suh S, Lee MK. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases in Korea. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2014;21 Suppl 1:S31–S35. - PubMed
-
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) JAMA. 2001;285(19):2486–2497. - PubMed
-
- Kang YH, Min HG, Kim IJ, Kim YK, Son SM. Comparison of alanine aminotransferase, white blood cell count, and uric acid in their association with metabolic syndrome: a study of Korean adults. Endocr J. 2008;55(6):1093–1102. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

