Proteomic profiling of human sera for discovery of potential biomarkers to monitor abstinence from alcohol abuse
- PMID: 25475211
- PMCID: PMC4492280
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201400319
Proteomic profiling of human sera for discovery of potential biomarkers to monitor abstinence from alcohol abuse
Abstract
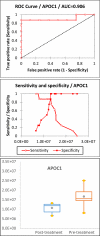
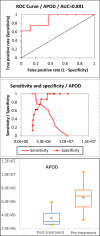
Although numerous biomarkers or biomarker candidates have been discovered to detect levels of drinking and intervals of time after last drinking episode, only a few biomarkers have been applied to monitor abstinence in a longer interval (≥6 wks) from alcohol abuse. Considering sample sources, sensitivity, and specificity, new biomarkers from blood with better accuracy are needed. To address this, serum proteomic profiles were compared between pre- and post- treatment samples from subjects seeking treatment for alcohol abuse and dependence in an intensive 6 wk daily outpatient program using high-abundance plasma protein immunodepletion and LC-MS/MS techniques. Protein identification, quantification, candidate biomarker selection, and prioritization analyses were carried out. Among the 246 quantified serum proteins, abundance of 13 and 45 proteins in female and male subjects were significantly changed (p ≤ 0.05), respectively. Of these biomarker candidate proteins, 2 (female) and 8 (male) proteins were listed in category 1, with high area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, sensitivity, specificity, and fold change. In summary, several new biomarker candidates have been identified to monitor abstinence from alcohol abuse.
Keywords: Alcohol Abuse; Biomarker; MS/MS; Proteomics.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A proteomic workflow for discovery of serum carrier protein-bound biomarker candidates of alcohol abuse using LC-MS/MS.Electrophoresis. 2009 Jun;30(12):2207-14. doi: 10.1002/elps.200800775. Electrophoresis. 2009. PMID: 19544491 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS-based serum proteomics for identification of candidate biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma.Proteomics. 2015 Jul;15(13):2369-81. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400364. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25778709 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in 1000 Human Plasma Samples with Mass Spectrometry.J Proteome Res. 2016 Feb 5;15(2):389-99. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00901. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Proteome Res. 2016. PMID: 26620284
-
The proteomic advantage: label-free quantification of proteins expressed in bovine milk during experimentally induced coliform mastitis.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010 Dec 15;138(4):252-66. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 21067814 Review.
-
Proteomics technologies for the global identification and quantification of proteins.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2010;80:1-44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381264-3.00001-1. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2010. PMID: 21109216 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA biomarkers for alcohol use disorder.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Nov 4;15:1032362. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1032362. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36407766 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Room R, Babor T, Rehm J. Lancet. 2005;365:519–530. - PubMed
-
- Mathurin P. Liver Transpl. 2005;11:S21–S24. - PubMed
-
- Kasinathan C, Vrana K, Beretta L, Thomas P, Gooch R, Worst T, Walker S, Xu A, Pierre P, Green H, Grant K, Manowitz P. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004;28:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Wu D, Tomonaga T, Sogawa K, Satoh M, Sunaga M, Nezu M, Oh-Ishi M, Kodera Y, Maeda T, Ochiai T, Nomura F. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007;31:S67–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

