Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, combined with metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 16-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial
- PMID: 25475929
- PMCID: PMC6680285
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.12424
Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, combined with metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 16-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial
Abstract
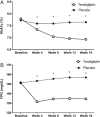
The aim of the present study was to assess the efficacy and safety of teneligliptin in combination with metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy. Patients [glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) 7.0-10.0%, on stable metformin ≥1000 mg/day] were randomized 2 : 1 to receive 20 mg teneligliptin plus metformin (n = 136) or placebo plus metformin (n = 68). The primary endpoint was the change in HbA1c levels from baseline to week 16. The mean baseline HbA1c was 7.9% in the teneligliptin group and 7.8% in the placebo group. The differences between the teneligliptin and placebo groups regarding changes in HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose levels were -0.78 % and -1.24 mmol/l (22.42 mg/dl), respectively, at week 16. The incidence of adverse events was similar between the groups. The addition of teneligliptin once daily to metformin was effective and generally well tolerated in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: DPP-4 inhibitors; Korean; metformin; teneligliptin.
© 2014 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to report.
B. C. and W. J. participated in designing the study. E. R., K. H., A. W., M. L., B. K., C. C., K. K., H. L., I. P., J. P., H. J., K. P., B. C. conducted the study and collected the data. W. J. analysed the data. M. K. and E. R. wrote the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Goda M, Kadowaki T. Teneligliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Drugs Today (Barc) 2013; 49: 615–629. - PubMed
-
- Nabeno M, Akahoshi F, Kishida H et al. A comparative study of the binding modes of recently launched dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors in the active site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 434: 191–196. - PubMed
-
- Eto T, Inoue S, Kadowaki T. Effects of once‐daily teneligliptin on 24‐h blood glucose control and safety in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 4‐week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2012; 14: 1040–1046. - PubMed
-
- Scott R, Loeys T, Davies MJ, Engel SS, Sitagliptin Study 801 Group . Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2008; 10: 959–969. - PubMed
-
- Bosi E, Camisasca RP, Collober C, Rochotte E, Garber AJ. Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control over 24 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: 890–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

