Tissue-specific actions of the metabolic hormones FGF15/19 and FGF21
- PMID: 25476453
- PMCID: PMC4277911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.10.002
Tissue-specific actions of the metabolic hormones FGF15/19 and FGF21
Abstract
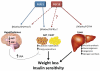
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) 15/19 and 21 belong to a subfamily of FGFs that function as hormones. Produced in response to specific nutritional cues, they act on overlapping sets of cell surface receptors composed of classic FGF receptors in complex with βKlotho, and regulate metabolism and related processes during periods of fluctuating energy availability. Pharmacologically, both FGF15/19 and FGF21 cause weight loss and improve both insulin-sensitivity and lipid parameters in rodent and primate models of metabolic disease. Recently, FGF21 was shown to have similar effects in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. We discuss here emerging concepts in FGF15/19 and FGF21 tissue-specific actions and critically assess their putative role as candidate targets for treating metabolic disease.
Keywords: arginine vasopressin; brown adipose tissue; corticotropin-releasing factor; hypothalamus; sympathetic nervous system; βKlotho.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Kliewer SA. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005;2:217–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

