Sensitivity and specificity of the hyperdense artery sign for arterial obstruction in acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 25477225
- PMCID: PMC4338528
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007036
Sensitivity and specificity of the hyperdense artery sign for arterial obstruction in acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background and purpose: In acute ischemic stroke, the hyperdense artery sign (HAS) on noncontrast computed tomography (CT) is thought to represent intraluminal thrombus and, therefore, is a surrogate of arterial obstruction. We sought to assess the accuracy of HAS as a marker of arterial obstruction by thrombus.
Methods: The Third International Stroke Trial (IST-3) was a randomized controlled trial testing the use of intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in patients who did not clearly meet the prevailing license criteria. Some participating IST-3 centers routinely performed CT or MR angiography at baseline. One reader assessed all relevant scans independently, blinded to all other data; we checked observer reliability. We combined IST-3 data with a systematic review and meta-analysis of all studies that assessed the accuracy of HAS using angiography (any modality).
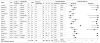
Results: IST-3 had 273 patients with baseline CT or MR angiography and was the largest study of HAS accuracy. The meta-analysis (n=902+273=1175, including IST-3) found sensitivity and specificity of HAS for arterial obstruction on angiography to be 52% and 95%, respectively. HAS was more commonly identified in proximal than distal arteries (47% versus 37%; P=0.015), and its sensitivity increased with thinner CT slices (r=-0.73; P=0.001). Neither extent of obstruction nor time after stroke influenced HAS accuracy.
Conclusions: When present in acute ischemic stroke, HAS indicates a high likelihood of arterial obstruction, but its absence indicates only a 50/50 chance of normal arterial patency. Thin-slice CT improves sensitivity of HAS detection.
Clinical trial registration url: http://www.controlled-trials.com/ISRCTN25765518. Unique identifier: ISRCTN25765518.
Keywords: angiography; meta-analysis; stroke.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Gacs G, Fox AJ, Barnett HJ, Vinuela F. CT visualization of intracranial arterial thromboembolism. Stroke. 1983;14:756–62. - PubMed
-
- Pressman BD, Tourje EJ, Thompson JR. An early CT sign of ischaemic infarction: increased density in a cerebral artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1987;8:645–8. - PubMed
-
- Koo CK, Teasdale E, Muir KW. What constitutes a true hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign? Cerebrovasc Dis. 2000;10:419–23. - PubMed

