Radical S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) enzymes in cofactor biosynthesis: a treasure trove of complex organic radical rearrangement reactions
- PMID: 25477515
- PMCID: PMC4326808
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R114.623793
Radical S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) enzymes in cofactor biosynthesis: a treasure trove of complex organic radical rearrangement reactions
Abstract
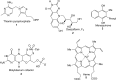
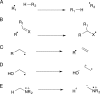
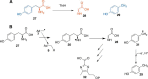
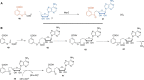
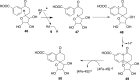
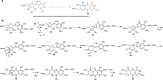
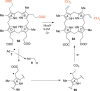
In this minireview, we describe the radical S-adenosylmethionine enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of thiamin, menaquinone, molybdopterin, coenzyme F420, and heme. Our focus is on the remarkably complex organic rearrangements involved, many of which have no precedent in organic or biological chemistry.
Keywords: Biosynthesis; Deazaflavin; Enzyme Mechanism; Heme; Menaquinone; Molybdopterin; Rearrangement; S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM); Thiamin; radical.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Sofia H. J., Chen G., Hetzler B. G., Reyes-Spindola J. F., Miller N. E. (2001) Radical SAM, a novel protein superfamily linking unresolved steps in familiar biosynthetic pathways with radical mechanisms: functional characterization using new analysis and information visualization methods. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 1097–1106 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkinson J. K., Ingold K. U. (1993) Cytochrome P450 hydroxylation of hydrocarbons: variation in the rate of oxygen rebound using cyclopropyl radical clocks including two new ultrafast probes. Biochemistry 32, 9209–9214 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

