Phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) in EMR-linked pediatric cohorts, genetically links PLCL1 to speech language development and IL5-IL13 to Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- PMID: 25477900
- PMCID: PMC4235428
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00401
Phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) in EMR-linked pediatric cohorts, genetically links PLCL1 to speech language development and IL5-IL13 to Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
Objective: We report the first pediatric specific Phenome-Wide Association Study (PheWAS) using electronic medical records (EMRs). Given the early success of PheWAS in adult populations, we investigated the feasibility of this approach in pediatric cohorts in which associations between a previously known genetic variant and a wide range of clinical or physiological traits were evaluated. Although computationally intensive, this approach has potential to reveal disease mechanistic relationships between a variant and a network of phenotypes.
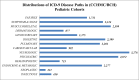
Method: Data on 5049 samples of European ancestry were obtained from the EMRs of two large academic centers in five different genotyped cohorts. Recently, these samples have undergone whole genome imputation. After standard quality controls, removing missing data and outliers based on principal components analyses (PCA), 4268 samples were used for the PheWAS study. We scanned for associations between 2476 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) with available genotyping data from previously published GWAS studies and 539 EMR-derived phenotypes. The false discovery rate was calculated and, for any new PheWAS findings, a permutation approach (with up to 1,000,000 trials) was implemented.
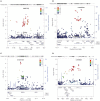
Results: This PheWAS found a variety of common variants (MAF > 10%) with prior GWAS associations in our pediatric cohorts including Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA), Asthma, Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) and Type 1 Diabetes with a false discovery rate < 0.05 and power of study above 80%. In addition, several new PheWAS findings were identified including a cluster of association near the NDFIP1 gene for mental retardation (best SNP rs10057309, p = 4.33 × 10(-7), OR = 1.70, 95%CI = 1.38 - 2.09); association near PLCL1 gene for developmental delays and speech disorder [best SNP rs1595825, p = 1.13 × 10(-8), OR = 0.65(0.57 - 0.76)]; a cluster of associations in the IL5-IL13 region with Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) [best at rs12653750, p = 3.03 × 10(-9), OR = 1.73 95%CI = (1.44 - 2.07)], previously implicated in asthma, allergy, and eosinophilia; and association of variants in GCKR and JAZF1 with allergic rhinitis in our pediatric cohorts [best SNP rs780093, p = 2.18 × 10(-5), OR = 1.39, 95%CI = (1.19 - 1.61)], previously demonstrated in metabolic disease and diabetes in adults.
Conclusion: The PheWAS approach with re-mapping ICD-9 structured codes for our European-origin pediatric cohorts, as with the previous adult studies, finds many previously reported associations as well as presents the discovery of associations with potentially important clinical implications.
Keywords: ICD-9 code; PheWAS; genetic polymorphism.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

