Antipsychotic Polypharmacy in Clozapine Resistant Schizophrenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Tapering Antipsychotic Co-treatment
- PMID: 25478102
- PMCID: PMC4253370
- DOI: 10.4081/mi.2012.e1
Antipsychotic Polypharmacy in Clozapine Resistant Schizophrenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Tapering Antipsychotic Co-treatment
Abstract
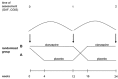
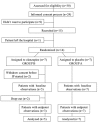
There is a considerable disparity between clinical practice and recommendations based on meta-analyses of antipsychotic polypharmacy in clozapine resistant schizophrenia. For this reason, we investigated the clinical response to reducing the use olanzapine that had been previously added on clozapine treatment among seriously ill hospitalized patients. In a randomized controlled trial with crossover design, we studied volunteer patients (N=15) who had olanzapine added on to clozapine in a state mental hospital. Clozapine monotherapy was just as effective as clozapine-olanzapine therapy, according to results from Clinical Global Impression Scale and Global Assessment of Functioning as primary outcome measures. Polypharmacy is widely used in treating schizophrenia, and usually, add-on medications are started because of worsening of the clinical state. A major confounding feature of these add-ons is whether observed improvements are caused by the medication or explained by the natural fluctuating course of the disorder. The present study, in spite of its small size, indicates the necessity of reconsidering the value of polypharmacy in treating schizophrenia.
Keywords: antipsychotics; clozapine; clozapine resistant schizophrenia; polypharmacy; randomized controlled trial.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Dr. Hallikainen has served as a consultant to Lundbeck and Novartis of Finland, and has received lecture fees from Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Lundbeck, Janssen-Cilag, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Novartis, and Sandoz. Dr. Tiihonen has served as a consultant to Lundbeck, Organon, Janssen-Cilag, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, F. Hoffman-La Roche and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and has received fees for giving expert opinions to Bristol-Myers Squibb and GlaxoSmithKline, in addition to lecture fees from Janssen-Cilag, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Lundbeck, GlaxoSmithKline and Astra Zeneca.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Antipsychotic Polypharmacy vs Monotherapy With Psychiatric Rehospitalization Among Adults With Schizophrenia.JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 May 1;76(5):499-507. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.4320. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30785608 Free PMC article.
-
The risks and benefits of switching patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder from two to one antipsychotic medication: a randomized controlled trial.Schizophr Res. 2015 Aug;166(1-3):194-200. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2015.05.038. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Schizophr Res. 2015. PMID: 26141142 Clinical Trial.
-
Outcomes of medicaid beneficiaries with schizophrenia receiving clozapine only or antipsychotic combinations.Psychiatr Serv. 2015 Feb 1;66(2):127-33. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201300085. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Psychiatr Serv. 2015. PMID: 25321616
-
The acute efficacy of antipsychotics in schizophrenia: a review of recent meta-analyses.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2018 Oct 8;8(11):303-318. doi: 10.1177/2045125318781475. eCollection 2018 Nov. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30344997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A critical review of atypical antipsychotic utilization: comparing monotherapy with polypharmacy and augmentation.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Feb;11(3):313-27. doi: 10.2174/0929867043456070. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 14965234 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical experiences of guided tapering of antipsychotics for patients with schizophrenia- a case series.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Mar 29;24(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05699-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38553687 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of pharmacological interventions for schizophrenia non-responsive to prior treatment: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Jun 7;84:103291. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103291. eCollection 2025 Jun. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40535000 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotic combinations for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 28;6(6):CD009005. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009005.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28658515 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotic polypharmacy reduction versus polypharmacy continuation for people with schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 30;8(8):CD014383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36042158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hegarty JD, Baldessarini RJ, Tohen M, et al. One hundred years of schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of the outcome literature. Am J Psychiatry 1994;151:1409-16. - PubMed
-
- Conley RR, Kelly DL.Management of treatment resistance in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2001;50:898-911. - PubMed
-
- Kane JM, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H.Clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenics. Psychopharmacol Bull 1988;24:62-7. - PubMed
-
- Meltzer HY.Treatment of the neuroleptic-nonresponsive schizophrenic patient. Schizophr Bull 1992;18:515-42. - PubMed
-
- Stahl SM, Grady MM.A critical review of atypical antipsychotic utilization: comparing monotherapy with polypharmacy and augmentation. Curr Med Chem 2004;11:313-27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources