Sex hormones and immune dimorphism
- PMID: 25478584
- PMCID: PMC4251360
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/159150
Sex hormones and immune dimorphism
Abstract
The functioning of the immune system of the body is regulated by many factors. The abnormal regulation of the immune system may result in some pathological conditions. Sex hormones of reproductive system are one of the major factors that regulate immune system due to the presence of hormone receptors on immune cells. The interaction of sex hormones and immune cells through the receptors on these cells effect the release of cytokines which determines the proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of different types of immunocytes and as a result the outcome of inflammatory or autoimmune diseases. The different regulations of sex hormones in both sexes result in immune dimorphism. In this review article the mechanism of regulation of immune system in different sexes and its impact are discussed.
Figures
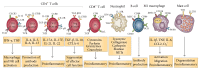

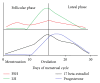
References
-
- Berczi I., Nagy E. Immune Modulating Agents. New York, NY, USA: Marcel Dekker; 1998.
-
- Barakonyi A., Polgar B., Szekeres-Bartho J. The role of γ/δ T-cell receptor-positive cells in pregnancy: part II. The American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. 1999;42(2):83–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

