A mutation in cnot8, component of the Ccr4-not complex regulating transcript stability, affects expression levels of developmental regulators and reveals a role of Fgf3 in development of caudal hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 25478689
- PMCID: PMC4257555
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113829
A mutation in cnot8, component of the Ccr4-not complex regulating transcript stability, affects expression levels of developmental regulators and reveals a role of Fgf3 in development of caudal hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons
Abstract
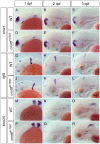
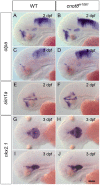
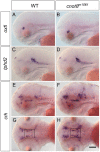
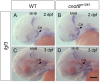
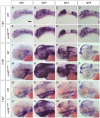
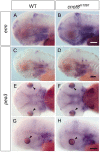
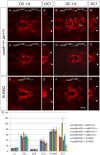
While regulation of the activity of developmental control genes at the transcriptional level as well as by specific miRNA-based degradation are intensively studied, little is known whether general cellular mechanisms controlling mRNA decay may contribute to differential stability of mRNAs of developmental control genes. Here, we investigate whether a mutation in the deadenylation dependent mRNA decay pathway may reveal differential effects on developmental mechanisms, using dopaminergic differentiation in the zebrafish brain as model system. In a zebrafish genetic screen aimed at identifying genes controlling dopaminergic neuron development we isolated the m1061 mutation that selectively caused increased dopaminergic differentiation in the caudal hypothalamus, while other dopaminergic groups were not affected. Positional cloning revealed that m1061 causes a premature stop codon in the cnot8 open reading frame. Cnot8 is a component of the Ccr4-Not complex and displays deadenylase activity, which is required for removal of the poly (A) tail in bulk mRNA turnover. Analyses of expression of developmental regulators indicate that loss of Cnot8 activity results in increased mRNA in situ hybridization signal levels for a subset of developmental control genes. We show that in the area of caudal hypothalamic dopaminergic differentiation, mRNA levels for several components of the FGF signaling pathway, including Fgf3, FGF receptors, and FGF target genes, are increased. Pharmacological inhibition of FGF signaling or a mutation in the fgf3 gene can compensate the gain of caudal hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons in cnot8m1061 mutants, indicating a role for Fgf3 in control of development of this dopaminergic population. The cnot8m1061 mutant phenotype provides an in vivo system to study roles of the Cnot8 deadenylase component of the mRNA decay pathway in vertebrate development. Our data indicate that attenuation of Cnot8 activity differentially affects mRNA levels of developmental control genes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effect of lead exposure on gene expression of Fgf3 in zebrafish embryonic development].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2012 Oct;30(10):730-4. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23256995 Chinese.
-
Tight transcriptional control of the ETS domain factors Erm and Pea3 by Fgf signaling during early zebrafish development.Mech Dev. 2001 Sep;107(1-2):105-17. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(01)00456-7. Mech Dev. 2001. PMID: 11520667
-
Fgf-dependent otic induction requires competence provided by Foxi1 and Dlx3b.BMC Dev Biol. 2007 Jan 19;7:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-5. BMC Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17239227 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Early Lymphocyte Development via mRNA Decay Catalyzed by the CCR4-NOT Complex.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 19;12:715675. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.715675. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34349771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of the dopamine systems in zebrafish.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;651:1-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-0322-8_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19731546 Review.
Cited by
-
New insights into the evolution of CAF1 family and utilization of TaCAF1Ia1 specificity to reveal the origin of the maternal progenitor for common wheat.J Adv Res. 2022 Dec;42:135-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.04.003. Epub 2022 Apr 13. J Adv Res. 2022. PMID: 36513409 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Deadenylase Genetic Association Network and Transcriptome Analysis in Thoracic Carcinomas.Molecules. 2022 May 12;27(10):3102. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103102. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35630580 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal function of the mRNA decapping complex determines survival of Caenorhabditis elegans at high temperature through temporal regulation of heterochronic gene expression.Open Biol. 2017 Mar;7(3):160313. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160313. Open Biol. 2017. PMID: 28250105 Free PMC article.
-
Fgf3 is crucial for the generation of monoaminergic cerebrospinal fluid contacting cells in zebrafish.Biol Open. 2019 Jun 5;8(6):bio040683. doi: 10.1242/bio.040683. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31036752 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish as a model to investigate the CRH axis and interactions with DISC1.Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 2022 Oct;26:100383. doi: 10.1016/j.coemr.2022.100383. Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 2022. PMID: 36632608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schier AF (2007) The Maternal-Zygotic Transition: Death and Birth of RNAs. 316:406–407. - PubMed
-
- Tadros W, Lipshitz HD (2005) Setting the stage for development: mRNA translation and stability during oocyte maturation and egg activation inDrosophila. 232:593–608. - PubMed
-
- Garneau NL, Wilusz J, Wilusz CJ (2007) The highways and byways of mRNA decay. 8:113–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

