rMATS: robust and flexible detection of differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data
- PMID: 25480548
- PMCID: PMC4280593
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1419161111
rMATS: robust and flexible detection of differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data
Abstract
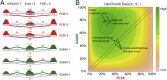
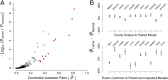
Ultra-deep RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) has become a powerful approach for genome-wide analysis of pre-mRNA alternative splicing. We previously developed multivariate analysis of transcript splicing (MATS), a statistical method for detecting differential alternative splicing between two RNA-Seq samples. Here we describe a new statistical model and computer program, replicate MATS (rMATS), designed for detection of differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data. rMATS uses a hierarchical model to simultaneously account for sampling uncertainty in individual replicates and variability among replicates. In addition to the analysis of unpaired replicates, rMATS also includes a model specifically designed for paired replicates between sample groups. The hypothesis-testing framework of rMATS is flexible and can assess the statistical significance over any user-defined magnitude of splicing change. The performance of rMATS is evaluated by the analysis of simulated and real RNA-Seq data. rMATS outperformed two existing methods for replicate RNA-Seq data in all simulation settings, and RT-PCR yielded a high validation rate (94%) in an RNA-Seq dataset of prostate cancer cell lines. Our data also provide guiding principles for designing RNA-Seq studies of alternative splicing. We demonstrate that it is essential to incorporate biological replicates in the study design. Of note, pooling RNAs or merging RNA-Seq data from multiple replicates is not an effective approach to account for variability, and the result is particularly sensitive to outliers. The rMATS source code is freely available at rnaseq-mats.sourceforge.net/. As the popularity of RNA-Seq continues to grow, we expect rMATS will be useful for studies of alternative splicing in diverse RNA-Seq projects.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; alternative splicing; exon; isoform; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Keren H, Lev-Maor G, Ast G. Alternative splicing and evolution: Diversification, exon definition and function. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(5):345–355. - PubMed
-
- Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ, Blencowe BJ. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat Genet. 2008;40(12):1413–1415. - PubMed
-
- Wang GS, Cooper TA. Splicing in disease: Disruption of the splicing code and the decoding machinery. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8(10):749–761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

