Integration of oncology and palliative care: a systematic review
- PMID: 25480826
- PMCID: PMC4294615
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0312
Integration of oncology and palliative care: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Both the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the European Society for Medical Oncology strongly endorse integrating oncology and palliative care (PC); however, a global consensus on what constitutes integration is currently lacking. To better understand what integration entails, we conducted a systematic review to identify articles addressing the clinical, educational, research, and administrative indicators of integration.
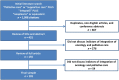
Materials and methods: We searched Ovid MEDLINE and Ovid EMBase between 1948 and 2013. Two researchers independently reviewed each citation for inclusion and extracted the indicators related to integration. The inter-rater agreement was high (κ = 0.96, p < .001).
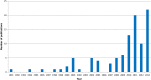
Results: Of the 431 publications in our initial search, 101 were included. A majority were review articles (58%) published in oncology journals (59%) and in or after 2010 (64%, p < .001). A total of 55 articles (54%), 33 articles (32%), 24 articles (24%), and 14 articles (14%) discussed the role of outpatient clinics, community-based care, PC units, and inpatient consultation teams in integration, respectively. Process indicators of integration include interdisciplinary PC teams (n = 72), simultaneous care approach (n = 71), routine symptom screening (n = 25), PC guidelines (n = 33), care pathways (n = 11), and combined tumor boards (n = 10). A total of 66 articles (65%) mentioned early involvement of PC, 18 (18%) provided a specific timing, and 28 (28%) discussed referral criteria. A total of 45 articles (45%), 20 articles (20%), and 66 articles (65%) discussed 8, 4, and 9 indicators related to the educational, research, and administrative aspects of integration, respectively.
Conclusion: Integration was a heterogeneously defined concept. Our systematic review highlighted 38 clinical, educational, research, and administrative indicators. With further refinement, these indicators may facilitate assessment of the level of integration of oncology and PC.
Keywords: Access; Health systems; Indicators; Integration; Neoplasms; Palliative care; Referral.
©AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Toward eubiosia: bridging oncology and palliative care.Oncologist. 2015 Jan;20(1):5-6. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0462. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 25492921 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating palliative care and oncology: towards a common understanding.Ann Palliat Med. 2015 Jan;4(1):3-4. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2224-5820.2015.02.01. Ann Palliat Med. 2015. PMID: 25813413 No abstract available.
-
Integration of Oncology and Palliative Care, a Forgotten Indicator: Shared Decision-Making.Oncologist. 2015 Sep;20(9):e26. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0131. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 26253556 Free PMC article.
-
In Reply.Oncologist. 2015 Sep;20(9):e27. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0146. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 26253557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hui D, Bruera E. Supportive and palliative oncology: A new paradigm for comprehensive cancer care. Oncol Hematol Rev. 2013;9:68–74.
-
- Yennurajalingam S, Urbauer DL, Casper KL, et al. Impact of a palliative care consultation team on cancer-related symptoms in advanced cancer patients referred to an outpatient supportive care clinic. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2011;41:49–56. - PubMed
-
- Temel JS, Greer JA, Muzikansky A, et al. Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:733–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical