Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A gene in Antheraea pernyi (Lepdoptera: Saturniidae)
- PMID: 25480968
- PMCID: PMC5633915
- DOI: 10.1093/jisesa/ieu030
Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A gene in Antheraea pernyi (Lepdoptera: Saturniidae)
Abstract
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A (eIF-4A) is an essential component for protein translation in eukaryotes. The eIF-4A gene (ApeIF-4A) was isolated and characterized from Antheraea pernyi (Guérin-Méneville) (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). The obtained cDNA sequence was 1,435-bp long with an open reading frame of 1,266 bp encoding 421 amino acids. The predicted amino acid sequence shared several conserved features as found in known eIF-4As and revealed 74 and 78% identities with eIF-4As of Homo sapiens L. and Drosophila melanogaster (Meigen), respectively. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis showed that ApeIF-4A was transcribed at four developmental stages and in all tissues tested, suggesting that it plays an important role in development of A. pernyi. Homologous alignment suggested that eIF-4As are highly conserved throughout evolution of eukaryote organisms. Phylogenetic trees based on the amino acid and nucleotide sequences of eIF-4A demonstrated a similar topology with the classical systematics, suggesting that it has the potential value in phylogenetic inference of eukaryotes.
Keywords: Antheraea pernyi; eukaryotic initiation factor 4A; expression pattern; phylogenetic inference.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Entomological Society of America.
Figures
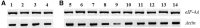


Similar articles
-
cDNA cloning and expression pattern of homolog of alpha subunit of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase Ib from the Chinese oak silkworm, Antheraea pernyi.J Insect Sci. 2011;11:148. doi: 10.1673/031.011.14801. J Insect Sci. 2011. PMID: 22224584 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning, expression pattern and phylogenetic analysis of the will die slowly gene from the Chinese oak silkworm, Antheraea pernyi.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Aug;38(6):3795-803. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0495-2. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21104437
-
cDNA cloning and expression pattern of two enolase genes from the Chinese oak silkworm, Antheraea pernyi.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2010 Nov;42(11):816-26. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmq084. Epub 2010 Oct 5. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2010. PMID: 20923858
-
Sex pheromones and olfactory proteins in Antheraea moths: A. pernyi and A. polyphemus (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae).Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020 Oct;105(2):e21729. doi: 10.1002/arch.21729. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32761939 Review.
-
Antheraea pernyi (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) and Its Importance in Sericulture, Food Consumption, and Traditional Chinese Medicine.J Econ Entomol. 2017 Aug 1;110(4):1404-1411. doi: 10.1093/jee/tox140. J Econ Entomol. 2017. PMID: 28535207 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Characterization of a Novel Microvitellogenin from the Chinese Oak Silkworm Antheraea pernyi.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 30;10(6):e0131751. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131751. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26126120 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an Ecdysteroid-Regulated 16 kDa Protein Gene in Chinese Oak Silkworm, Antheraea pernyi (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae).J Insect Sci. 2020 May 1;20(3):4. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieaa033. J Insect Sci. 2020. PMID: 32396202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danforth B. N., Fang J., Sipes S. . 2006. . Analysis of family-level relationships in bees (Hymenoptera: Apiformes) using 28S and two previously unexplored nuclear genes: CAD and RNA polymerase II . Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 39 : 358 – 372 . - PubMed
-
- Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Satler C. A., Merrick W. C. . 1984. . RNA-stimulated ATPase activity of eukaryotic initiation factors . J. Biol. Chem. 259 : 8648 – 8654 . - PubMed
-
- Hernández G., Lalioti V., Vandekerckhove J., Sierra J. M., Santarén J. F. . 2004. . Identification and characterization of the expression of the translation initiation factor 4A (eIF4A) from Drosophila melanogaster . Proteomics 4 : 316 – 326 . - PubMed
-
- Hou W.R., Sun G. L., Chen Y., Wu X., Peng Z. S., Zhou C. Q. . 2008. . Molecular cloning of ribosomal protein L26 (RPL26) cDNA from Ailuropoda melanoleuca and its potential value in phylogenetic study . Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 36 : 194 – 200 .
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

